Genome-scale activation screen identifies a lncRNA locus regulating a gene neighbourhood
- PMID: 28792927
- PMCID: PMC5706657
- DOI: 10.1038/nature23451
Genome-scale activation screen identifies a lncRNA locus regulating a gene neighbourhood
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Genome-scale activation screen identifies a lncRNA locus regulating a gene neighbourhood.Nature. 2017 Sep 20;549(7672):418. doi: 10.1038/nature24009. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28933431
Abstract
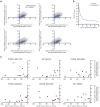
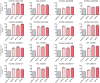
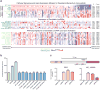
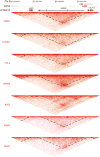
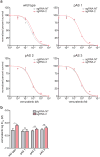
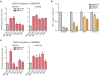
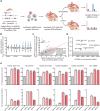
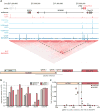
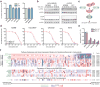
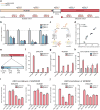
Mammalian genomes contain thousands of loci that transcribe long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), some of which are known to carry out critical roles in diverse cellular processes through a variety of mechanisms. Although some lncRNA loci encode RNAs that act non-locally (in trans), there is emerging evidence that many lncRNA loci act locally (in cis) to regulate the expression of nearby genes-for example, through functions of the lncRNA promoter, transcription, or transcript itself. Despite their potentially important roles, it remains challenging to identify functional lncRNA loci and distinguish among these and other mechanisms. Here, to address these challenges, we developed a genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 activation screen that targets more than 10,000 lncRNA transcriptional start sites to identify noncoding loci that influence a phenotype of interest. We found 11 lncRNA loci that, upon recruitment of an activator, mediate resistance to BRAF inhibitors in human melanoma cells. Most candidate loci appear to regulate nearby genes. Detailed analysis of one candidate, termed EMICERI, revealed that its transcriptional activation resulted in dosage-dependent activation of four neighbouring protein-coding genes, one of which confers the resistance phenotype. Our screening and characterization approach provides a CRISPR toolkit with which to systematically discover the functions of noncoding loci and elucidate their diverse roles in gene regulation and cellular function.
Figures
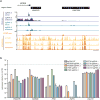
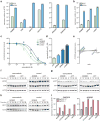
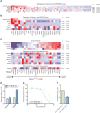
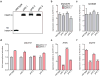
Comment in
-
Escaping BRAF inhibition: A "linc" with non-coding RNAs?Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2018 Mar;31(2):236-237. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12655. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2018. PMID: 28986964 No abstract available.
References
-
- Brown CJ, et al. The human XIST gene: analysis of a 17 kb inactive X-specific RNA that contains conserved repeats and is highly localized within the nucleus. Cell. 1992;71:527–542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

