Krüppel-Like Factor 4 Regulation of Cholesterol-25-Hydroxylase and Liver X Receptor Mitigates Atherosclerosis Susceptibility
- PMID: 28794002
- PMCID: PMC5741092
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.027462
Krüppel-Like Factor 4 Regulation of Cholesterol-25-Hydroxylase and Liver X Receptor Mitigates Atherosclerosis Susceptibility
Abstract
Background: Atherosclerosis is a multifaceted inflammatory disease involving cells in the vascular wall (eg, endothelial cells [ECs]), as well as circulating and resident immunogenic cells (eg, monocytes/macrophages). Acting as a ligand for liver X receptor (LXR), but an inhibitor of SREBP2 (sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2), 25-hydroxycholesterol, and its catalyzing enzyme cholesterol-25-hydroxylase (Ch25h) are important in regulating cellular inflammatory status and cholesterol biosynthesis in both ECs and monocytes/macrophages.
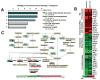
Methods: Bioinformatic analyses were used to investigate RNA-sequencing data to identify cholesterol oxidation and efflux genes regulated by Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4). In vitro experiments involving cultured ECs and macrophages and in vivo methods involving mice with Ch25h ablation were then used to explore the atheroprotective role of KLF4-Ch25h/LXR.
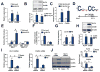
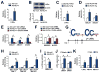
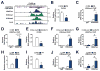
Results: Vasoprotective stimuli increased the expression of Ch25h and LXR via KLF4. The KLF4-Ch25h/LXR homeostatic axis functions through suppressing inflammation, evidenced by the reduction of inflammasome activity in ECs and the promotion of M1 to M2 phenotypic transition in macrophages. The increased atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-/-/Ch25h-/- mice further demonstrates the beneficial role of the KLF4-Ch25h/LXR axis in vascular function and disease.
Conclusions: KLF4 transactivates Ch25h and LXR, thereby promoting the synergistic effects between ECs and macrophages to protect against atherosclerosis susceptibility.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cholesterol; endothelial cells; inflammation; macrophages; shear stress.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

