Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements During Pregnancy and Lactation Did Not Affect Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Bioactive Proteins in a Randomized Trial
- PMID: 28794206
- PMCID: PMC5610548
- DOI: 10.3945/jn.117.252981
Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements During Pregnancy and Lactation Did Not Affect Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Bioactive Proteins in a Randomized Trial
Abstract
Background: Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) and bioactive proteins are beneficial to infant health. Recent evidence suggests that maternal nutrition may affect the amount of HMOs and proteins in breast milk; however, the effect of nutrient supplementation on HMOs and bioactive proteins has not yet been well studied.
Objective: We aimed to determine whether lipid-based nutrient supplements (LNSs) affect milk bioactive protein and HMO concentrations at 6 mo postpartum in women in rural Malawi. These are secondary outcomes of a previously published randomized controlled trial.
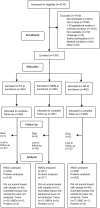
Methods: Women were randomly assigned to consume either an iron and folic acid capsule (IFA) daily from ≤20 wk gestation until delivery, followed by placebo daily from delivery to 6 mo postpartum, or a multiple micronutrient (MMN) capsule or LNS daily from ≤20 wk gestation to 6 mo postpartum. Breast milk concentrations of total HMOs, sialylated HMOs, fucosylated HMOs, lactoferrin, lactalbumin, lysozymes, antitrypsin, immunoglobulin A, and osteopontin were analyzed at 6 mo postpartum (n = 647). Between-group differences in concentrations and in proportions of women classified as having low concentrations were tested.
Results: HMO and bioactive protein concentrations did not differ between groups (P > 0.10 for all comparisons). At 6 mo postpartum, the proportions of women with low HMOs or bioactive proteins were not different between groups except for osteopontin. A lower proportion of women in the IFA group had low osteopontin compared with the LNS group after adjusting for covariates (OR: 0.5; 95% CI: 0.3, 0.9; P = 0.016).
Conclusion: The study findings do not support the hypothesis that supplementation with an LNS or MMN capsule during pregnancy and postpartum would increase HMO or bioactive milk proteins at 6 mo postpartum among Malawian women. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT01239693.
Keywords: bioactive breast milk proteins; human milk oligosaccharides; lactation; lipid-based nutrient supplements; multiple micronutrient supplements; postpartum.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures: JMJ, CA, PA, UA, DC, YBC, JCCD, Y-MF, EG, EK, CK, CBL, KM, SMT, LDW, and KGD, no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Victora CG, Bahl R, Barros AJ, Franca GV, Horton S, Krasevec J, Murch S, Sankar MJ, Walker N, Rollins NC, et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016;387:475–90. - PubMed
-
- De Leoz ML, Gaerlan SC, Strum JS, Dimapasoc LM, Mirmiran M, Tancredi DJ, Smilowitz JT, Kalanetra KM, Mills DA, German JB, et al. Lacto-N-tetraose, fucosylation, and secretor status are highly variable in human milk oligosaccharides from women delivering preterm. J Proteome Res 2012;11:4662–72. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lönnerdal B. Bioactive proteins in human milk: health, nutrition, and implications for infant formulas. J Pediatr 2016;173(Suppl):S4–9. - PubMed
-
- Pellegrini A, Thomas U, Bramaz N, Hunziker P, von Fellenberg R. Isolation and identification of three bactericidal domains in the bovine alpha-lactalbumin molecule. Biochim Biophys Acta 1999;1426:439–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials