Distributing pulse oximeter: An initiative for improving patient safety and care
- PMID: 28794534
- PMCID: PMC5530747
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_89_17
Distributing pulse oximeter: An initiative for improving patient safety and care
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
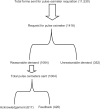
Figures
References
-
- Moller JT, Jensen PF, Johannessen NW, Espersen K. Hypoxaemia is reduced by pulse oximetry monitoring in the operating theatre and in the recovery room. Br J Anaesth. 1992;68:146–50. - PubMed
-
- Moller JT, Johannessen NW, Espersen K, Ravlo O, Pedersen BD, Jensen PF, et al. Randomized evaluation of pulse oximetry in 20,802 patients: II. Perioperative events and postoperative complications. Anesthesiology. 1993;78:445–53. - PubMed
-
- Bainbridge D, Martin J, Arango M, Cheng D. Evidence-based Peri-operative Clinical Outcomes Research (EPiCOR) Group. Perioperative and anaesthetic-related mortality in developed and developing countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2012;380:1075–81. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organisation. WHO Surgical Safety Checklist and Implementation Manual. [Last accessed on 2016 Apr 10]. Available from: http://www.who.int/patientsafety/safesurgery/ss_checklist/en/index.html .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources