Procalcitonin: a promising diagnostic marker for sepsis and antibiotic therapy
- PMID: 28794881
- PMCID: PMC5543591
- DOI: 10.1186/s40560-017-0246-8
Procalcitonin: a promising diagnostic marker for sepsis and antibiotic therapy
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is a global healthcare problem, characterized by whole body inflammation in response to microbial infection, which leads to organ dysfunction. It is becoming a frequent complication in hospitalized patients. Early and differential diagnosis of sepsis is needed critically to avoid unnecessary usage of antimicrobial agents and for proper antibiotic treatments through the screening of biomarkers that sustains with diagnostic significance.
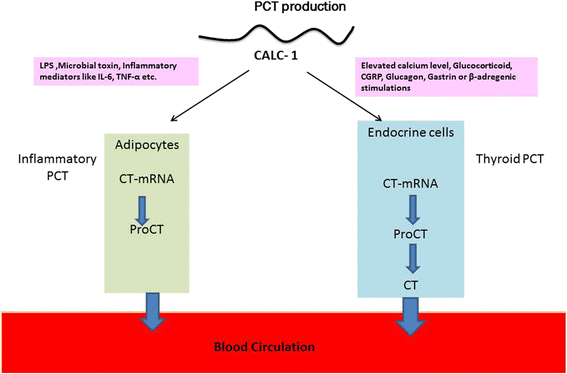
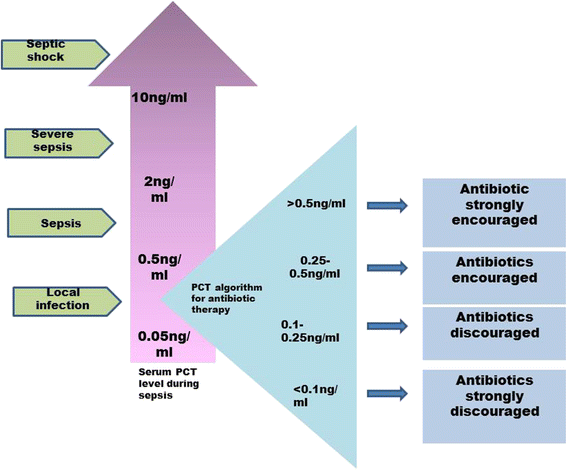
Main body of abstract: Current targeting conventional markers (C-reactive protein, white blood cell, tumour necrosis factor-α, interleukins, etc.) are non-specific for diagnosing sepsis. Procalcitonin (PCT), a member of the calcitonin super family could be a critical tool for the diagnosis of sepsis. But to distinguish between bacterial versus viral infections, procalcitonin alone may not be effective. Rapid elevation in the concentration of procalcitonin and other newly emerging biomarkers during an infection and its correlation with severity of illness makes it an ideal biomarker for bacterial infection. Beside this, the procalcitonin levels can be used for monitoring response to antimicrobial therapy, diagnosis of secondary inflammations, diagnosis of renal involvement in paediatric urinary tract infection, etc. The present article summarizes the relevance of procalcitonin in the diagnosis of sepsis and how it can be useful in determining the therapeutic approaches.
Conclusion: Further studies are needed to better understand the application of PCT in the diagnosis of sepsis, differentiating between microbial and non-microbial infection cases and determining the therapeutic approaches for sepsis.
Keywords: Antibiotic therapy; Diagnostic marker; Procalcitonin; Sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Ms. Ashitha Vijayan, M. Sc Microbiology, working as Research Intern in Diagnostic Products lab of CRDC, HLL and involved in diagnostic kit developments.
Ms. Vani Maya, M. Sc Biochemistry, working as Junior Project Fellow in Diagnostic Products lab of CRDC, HLL and involved in diagnostic kit developments.
Ms. Shilpa Ravindran, M. Sc Biochemistry, Working as Senior Project Fellow in Diagnostic Products lab of CRDC, HLL and involved in diagnostic kit developments.
Mr. Saikant R, M. Sc Biotechnology, working as Junior Scientist in Diagnostic Products lab of CRDC, HLL and involved in diagnostic kit developments.
Dr. Lakshmi S, Ph.D Biotechnology, working as Junior Scientist in Diagnostic Products lab of CRDC, HLL and involved in drug developments.
Dr. Kartik Ramaswami, Ph.D Biotechnology, working as Junior Scientist in Diagnostic Products lab of CRDC, HLL and involved in clinical research.
Dr. Manoj G, Ph. D Biotechnology, working as Scientist E2 in Diagnostic Products lab of CRDC, HLL and involved in diagnostic kit developments.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Lever A, Mackenzie I. Sepsis: definition, epidemiology, and diagnosis. Br Med J. 2007;335:879–883. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39346.495880.AE. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials