Sensitive Molecular Diagnostics for Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
- PMID: 28795077
- PMCID: PMC5543577
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofx037
Sensitive Molecular Diagnostics for Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Abstract
Background: Rapid diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) and identification of Leishmania species is highly important for the disease management. In Israel, CL is caused mainly by Leishmania major and Leishmania tropica species.
Methods: We established an easy to handle point of care lesion-swabbing, combined with a highly sensitive multiplex real time PCR (multiplex qPCR) for accurate and rapid diagnosis of Leishmania species.
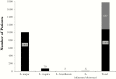
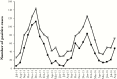
Results: Using three probes: one general for: Leishmania species, and two specific for L major, and L tropica, we screened 1783 clinical samples collected during two years. Leishmania species was found in 1086 individuals, 1008 L major, and 70 L tropica. Eight samples positive for Leishmania species only, were further tested using a second set of multiplex qPCR developed, and were found positive for Leishmania braziliensis and Leishmania infantum/donovani (2 and 6 samples, concomitantly).
Conclusions: Taken together, the test enabled diagnostics and better treatment of Leishmania infections from the Old World (1078 samples) and the New World (8 samples), and the subtyping of the dominant strains in the region, as well as in returning travelers'.
Keywords: Leishmania major; Leishmania species; qPCR; real-time PCR..
Figures

References
-
- Ben-Shimol S, Sagi O, Codish S, et al. Dramatic increase in laboratory-diagnosed human cutaneous leishmaniasis cases in southern Israel, 2007-2013. Infect Dis (Lond) 2015; 47:161–7. - PubMed
-
- Jaffe CL, Baneth G, Abdeen ZA, et al. Leishmaniasis in Israel and the Palestinian Authority. Trends Parasitol 2004; 20:328–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

