The Effects of Tacrolimus on T-Cell Proliferation Are Short-Lived: A Pilot Analysis of Immune Function Testing
- PMID: 28795150
- PMCID: PMC5540637
- DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000000715
The Effects of Tacrolimus on T-Cell Proliferation Are Short-Lived: A Pilot Analysis of Immune Function Testing
Abstract
Background: Optimal immunosuppression after organ transplant should balance the risks of rejection, infection, and malignancy while minimizing barriers to adherence including frequent or time-sensitive dosing. There is currently no reliable immune function assay to directly measure the degree of immunosuppression after transplantation.
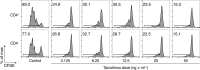
Methods: We developed an immune function assay to mea//sure T-cell proliferation after exposure to immunosuppression in vivo. We tested the assay in mice, and then piloted the approach using single time point samples, 11 pediatric kidney transplant recipients prescribed tacrolimus, mycophenolate, and prednisone 6 months to 5 years posttransplant, with no history of rejection, opportunistic infection, or cancer. Twelve healthy adults were controls.
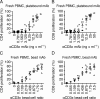
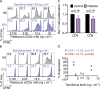
Results: We demonstrated that our assay can quantify suppression of murine T-cell proliferation after tacrolimus treatment in vivo. In humans, we found a mean 25% reduction in CD4 and CD8 T-cell proliferation in pediatric renal transplant recipients on triple immunosuppression compared with adult healthy controls, but the pilot results were not statistically significant nor correlated with serum tacrolimus levels. We observed that cell processing and washing reduced the effects of tacrolimus on T-cell proliferation, as did discontinuation of tacrolimus treatment shortly before sampling.
Conclusions: T-cell proliferation is currently not suitable to measure immunosuppression because sample processing diminishes observable effects. Future immune function testing should focus on fresh samples with minimal washing steps. Our results also emphasize the importance of adherence to immunosuppressive treatment, because T-cell proliferation recovered substantially after even brief discontinuation of tacrolimus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nankivell BJ, Alexander SI. Rejection of the kidney allograft. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1451–1462. - PubMed
-
- Foster BJ. Heightened graft failure risk during emerging adulthood and transition to adult care. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015;30:567–576. - PubMed
-
- Dharnidharka VR, Agodoa LY, Abbott KC. Risk factors for hospitalization for bacterial or viral infection in renal transplant recipients—an analysis of USRDS data. Am J Transplant. 2007;7:653–661. - PubMed
-
- Dharnidharka VR, Stablein DM, Harmon WE. Post-transplant infections now exceed acute rejection as cause for hospitalization: a report of the NAPRTCS. Am J Transplant. 2004;4:384–389. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

