There is no difference in outcome between laparoscopic and open surgery for rectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis on short- and long-term oncologic outcomes
- PMID: 28795243
- PMCID: PMC5602007
- DOI: 10.1007/s10151-017-1662-4
There is no difference in outcome between laparoscopic and open surgery for rectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis on short- and long-term oncologic outcomes
Abstract
Background: Until recently there has been little data available about long-term outcomes of laparoscopic rectal cancer surgery. But new randomized controlled trials regarding laparoscopic colorectal surgery have been published. The aim of this study was to compare the short- and long-term oncologic outcomes of laparoscopy and open surgery for rectal cancer through a systematic review of the literature and a meta-analysis of relevant RCTs.
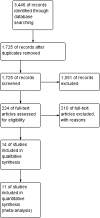
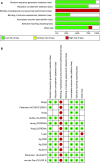
Methods: A systematic review of Medline, Embase and the Cochrane library from January 1966 to October 2016 with a subsequent meta-analysis was performed. Only randomized controlled trials with data on circumferential resection margins were included. The primary outcome was the status of circumferential resection margins. Secondary outcomes included lymph node yield, distal resection margins, disease-free and overall survival rates for 3 and 5 years and local recurrence rates.
Results: Eleven studies were evaluated, involving a total of 2018 patients in the laparoscopic group and 1526 patients in the open group. The presence of involved circumferential margins was reported in all studies. There were no statistically significant differences in the number of positive circumferential margins between the laparoscopic group and open group, RR 1.16, 95% CI 0.89-1.50 and no significant differences in involvement of distal margins (RR 1.13 95% CI 0.35-3.66), completeness of mesorectal excision (RR 1.22, 95% CI 0.82-1.82) or number of harvested lymph nodes (mean difference = -0.01, 95% CI -0.89 to 0.87). Disease-free survival rates at 3 and 5 years were not different (p = 0.26 and p = 0.71 respectively), and neither were overall survival rates (p = 0.19 and p = 0.64 respectively), nor local recurrence rates (RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.63-1.23).
Conclusions: Laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer is associated with similar short-term and long-term oncologic outcomes compared to open surgery. The oncologic quality of extracted specimens seems comparable regardless of the approach used.
Keywords: Circumferential resection margin; Laparoscopy; Local recurrence; Meta-analysis; Rectal cancer; Survival; Total mesorectal excision.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Figures









Comment in
-
Nearly complete TME quality conundrum.Tech Coloproctol. 2018 Mar;22(3):243. doi: 10.1007/s10151-017-1734-5. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Tech Coloproctol. 2018. PMID: 29236197 No abstract available.
-
Response to: the nearly complete TME quality conundrum.Tech Coloproctol. 2018 Mar;22(3):245-246. doi: 10.1007/s10151-018-1758-5. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Tech Coloproctol. 2018. PMID: 29476445 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- van de Velde CJ, Boelens PG, Borras JM, Coebergh JW, Cervantes A, Blomqvist L, et al. EURECCA colorectal: multidisciplinary management: European consensus conference colon & rectum. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(1):1.e–e34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

