linc00673 (ERRLR01) is a prognostic indicator of overall survival in breast cancer
- PMID: 28795861
- PMCID: PMC5791815
- DOI: 10.1080/21541264.2017.1329684
linc00673 (ERRLR01) is a prognostic indicator of overall survival in breast cancer
Abstract
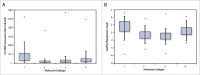
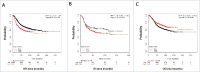
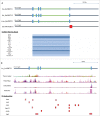
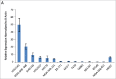
LncRNAs are novel noncoding RNAs involved in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression by recruiting ribonucleoprotein complexes to specific genomic loci to initiate histone methylation and/or other chromatin modifications. LncRNAs themselves function as tumor suppressors or oncogenes, depending on the gene regulatory networks they govern. We identified lnc00673 (ERRLR01) as a marker of overall survival (OS) in breast cancer patients. Specifically, ERRLR01 levels were elevated in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) as compared with Luminal-A, Luminal-B, and HER2 breast cancer subtypes. ERRLR01 levels were also inversely correlated with breast cancer survival across all breast cancer patients. Upon stratification, OS in ERα- tumors correlated with negative overall survival, while in ERα+ tumors, ERRLR01 correlated with positive outcomes. This suggests ERRLR01 is modulated by hormone signaling in breast cancer. Gene-network analysis revealed ERRLR01 correlated with distinct pathways including "epithelial development" and "cellular differentiation." These data suggest ERRLR01 operates as an oncogene in TNBC, as well as a biomarker in breast cancer patients.
Keywords: ERRLR01; breast cancer; estrogen signaling; hormone-regulation; lncRNA; survival outcomes.
Figures


References
-
- Rinn JL, Chang HY. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem 2012; 81:145–66; PMID:22663078; https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-051410-092902 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rinn JL. LncRNAs: Linking RNA to chromatin. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2014; 6:a018614; PMID:25085913; https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a018614 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huarte M. The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. Nat Med 2015; 21:1253–61; PMID:26540387; https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3981 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goff LA, Rinn JL. Linking RNA biology to lncRNAs. Genome Res 2015; 25:1456–65; PMID:26430155; https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.191122.115 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morris KV. Long antisense non-coding RNAs function to direct epigenetic complexes that regulate transcription in human cells. Epigenetics 2009; 4:296–301; https://doi.org/10.4161/epi.4.5.9282 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
