Dehydrothermally Cross-Linked Collagen Membrane with a Bone Graft Improves Bone Regeneration in a Rat Calvarial Defect Model
- PMID: 28796152
- PMCID: PMC5578293
- DOI: 10.3390/ma10080927
Dehydrothermally Cross-Linked Collagen Membrane with a Bone Graft Improves Bone Regeneration in a Rat Calvarial Defect Model
Abstract
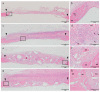
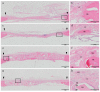
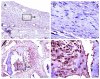
In this study, the bone regeneration efficacy of dehydrothermally (DHT) cross-linked collagen membrane with or without a bone graft (BG) material was evaluated in a critical-sized rat model. An 8-mm-diameter defect was created in the calvaria of 40 rats, which were randomized into four groups: (1) control; (2) DHT; (3) BG; and, (4) DHT + BG. Evaluations were made at 2 and 8 weeks after surgery using micro-computed tomographic (micro-CT), histological, and histomorphometric analyses. Micro-CT analysis showed an increase in the new bone volume (NBV) of the BG and DHT + BG groups at 2 weeks after surgery, representing a significant difference (p < 0.05). At 8 weeks after surgery, the NBV increased in all four groups. However, larger NBVs were observed in the BG and DHT + BG groups, and a significant difference was no longer observed between the two groups. Histologic analysis demonstrated that the graft materials sustained the center of the defect in the BG and DHT + BG groups, which was shown in histomorphometric analysis as well. These results suggest that DHT membrane is a safe biomaterial with adequate tissue integration, and has a positive effect on new bone formation. Moreover, the best effects were achieved when DHT was used in conjunction with BG materials.
Keywords: allograft; bone regeneration; collagen; cross-linking; dehydrothermal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Laino L., Iezzi G., Piattelli A., Lo Muzio L., Cicciu M. Vertical ridge augmentation of the atrophic posterior mandible with sandwich technique: Bone block from the chin area versus corticocancellous bone block allograft--clinical and histological prospective randomized controlled study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014;2014:982104. doi: 10.1155/2014/982104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rothamel D., Benner M., Fienitz T., Happe A., Kreppel M., Nickenig H.J., Zoller J.E. Biodegradation pattern and tissue integration of native and cross-linked porcine collagen soft tissue augmentation matrices—An experimental study in the rat. Head Face Med. 2014;10:10. doi: 10.1186/1746-160X-10-10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

