Genetic disruption of the oncogenic HMGA2-PLAG1-IGF2 pathway causes fetal growth restriction
- PMID: 28796236
- PMCID: PMC5846811
- DOI: 10.1038/gim.2017.105
Genetic disruption of the oncogenic HMGA2-PLAG1-IGF2 pathway causes fetal growth restriction
Abstract
PurposeFetal growth is a complex process involving maternal, placental and fetal factors. The etiology of fetal growth retardation remains unknown in many cases. The aim of this study is to identify novel human mutations and genes related to Silver-Russell syndrome (SRS), a syndromic form of fetal growth retardation, usually caused by epigenetic downregulation of the potent fetal growth factor IGF2.MethodsWhole-exome sequencing was carried out on members of an SRS familial case. The candidate gene from the familial case and two other genes were screened by targeted high-throughput sequencing in a large cohort of suspected SRS patients. Functional experiments were then used to link these genes into a regulatory pathway.ResultsWe report the first mutations of the PLAG1 gene in humans, as well as new mutations in HMGA2 and IGF2 in six sporadic and/or familial cases of SRS. We demonstrate that HMGA2 regulates IGF2 expression through PLAG1 and in a PLAG1-independent manner.ConclusionGenetic defects of the HMGA2-PLAG1-IGF2 pathway can lead to fetal and postnatal growth restriction, highlighting the role of this oncogenic pathway in the fine regulation of physiological fetal/postnatal growth. This work defines new genetic causes of SRS, important for genetic counseling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

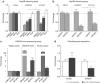

References
-
- Sheridan C. Intrauterine growth restriction—diagnosis and management. Aust Fam Physician 2005;34:717–723. - PubMed
-
- Dias RP, Nightingale P, Hardy C et al. Comparison of the clinical scoring systems in Silver-Russell syndrome and development of modified diagnostic criteria to guide molecular genetic testing. J Med Genet 2013;50:635–639. - PubMed
-
- Bartholdi D, Krajewska-Walasek M, Ounap K et al. Epigenetic mutations of the imprinted IGF2-H19 domain in Silver-Russell syndrome (SRS): results from a large cohort of patients with SRS and SRS-like phenotypes. J Med Genet 2009;46:192–197. - PubMed
-
- Netchine I, Rossignol S, Dufourg MN et al. 11p15 imprinting center region 1 loss of methylation is a common and specific cause of typical Russell-Silver syndrome: clinical scoring system and epigenetic-phenotypic correlations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:3148–3154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

