Biphasic ROS production, p53 and BIK dictate the mode of cell death in response to DNA damage in colon cancer cells
- PMID: 28796811
- PMCID: PMC5552129
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182809
Biphasic ROS production, p53 and BIK dictate the mode of cell death in response to DNA damage in colon cancer cells
Abstract
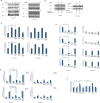
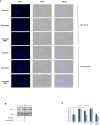
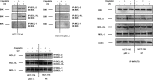
Necrosis, apoptosis and autophagic cell death are the main cell death pathways in multicellular organisms, all with distinct and overlapping cellular and biochemical features. DNA damage may trigger different types of cell death in cancer cells but the molecular events governing the mode of cell death remain elusive. Here we showed that increased BH3-only protein BIK levels promoted cisplatin- and UV-induced mitochondrial apoptosis and biphasic ROS production in HCT-116 wild-type cells. Nonetheless, early single peak of ROS formation along with lysosomal membrane permeabilization and cathepsin activation regulated cisplatin- and UV-induced necrosis in p53-null HCT-116 cells. Of note, necrotic cell death in p53-null HCT-116 cells did not depend on BIK, mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization or caspase activation. These data demonstrate how cancer cells with different p53 background respond to DNA-damaging agents by integrating distinct cell signaling pathways dictating the mode of cell death.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human melanoma cells selected for resistance to apoptosis by prolonged exposure to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand are more vulnerable to necrotic cell death induced by cisplatin.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Feb 15;12(4):1355-64. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2084. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16489094
-
p53-dependent and -independent mechanisms are involved in (E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(2-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (HMP)-induced apoptosis in HCT116 colon cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Oct 28;479(4):913-919. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.09.067. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27641669
-
A synthetic chalcone derivative, 2-hydroxy-3',5,5'-trimethoxychalcone (DK-139), triggers reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis independently of p53 in A549 lung cancer cells.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Jan 25;298:72-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.11.003. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 30408460
-
Reactive oxygen species regulation of autophagy in cancer: implications for cancer treatment.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Oct 1;53(7):1399-410. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.07.011. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22820461 Review.
-
[Lysosomal membrane permeabilization as apoptogenic factor].Tsitologiia. 2011;53(4):313-24. Tsitologiia. 2011. PMID: 21675210 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Chiauranib selectively inhibits colorectal cancer with KRAS wild-type by modulation of ROS through activating the p53 signaling pathway.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Nov 1;10(11):3666-3685. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33294260 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Mechanisms Involving in Radioresistance of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2020 Apr 25;11(14):4193-4204. doi: 10.7150/jca.39354. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32368302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial estrogen receptors alter mitochondrial priming and response to endocrine therapy in breast cancer cells.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Jul 22;7(1):189. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00573-2. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34294688 Free PMC article.
-
MyoD1 promotes the transcription of BIK and plays an apoptosis-promoting role in the development of gastric cancer.Cell Cycle. 2024 Mar;23(5):573-587. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2024.2348344. Epub 2024 May 3. Cell Cycle. 2024. PMID: 38701194 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and Cellular Characterization of New Radio-Resistant Cell Lines Reveals a Role of Natural Flavonoids to Bypass Senescence.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 28;23(1):301. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010301. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sarosiek KA, Ni Chonghaile T, Letai A. Mitochondria: gatekeepers of response to chemotherapy. Trends in cell biology. 2013;23(12):612–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.08.003 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3842421. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chinnadurai G, Vijayalingam S, Rashmi R. BIK, the founding member of the BH3-only family proteins: mechanisms of cell death and role in cancer and pathogenic processes. Oncogene. 2008;27 Suppl 1:S20–9. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.40 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2928562. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McDonnell JM, Fushman D, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ, Cowburn D. Solution structure of the proapoptotic molecule BID: a structural basis for apoptotic agonists and antagonists. Cell. 1999;96(5):625–34. . - PubMed
-
- Boyd JM, Gallo GJ, Elangovan B, Houghton AB, Malstrom S, Avery BJ, et al. Bik, a novel death-inducing protein shares a distinct sequence motif with Bcl-2 family proteins and interacts with viral and cellular survival-promoting proteins. Oncogene. 1995;11(9):1921–8. . - PubMed
-
- Germain M, Mathai JP, Shore GC. BH-3-only BIK functions at the endoplasmic reticulum to stimulate cytochrome c release from mitochondria. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2002;277(20):18053–60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M201235200 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

