Increased microRNA-93-5p inhibits osteogenic differentiation by targeting bone morphogenetic protein-2
- PMID: 28797104
- PMCID: PMC5552299
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182678
Increased microRNA-93-5p inhibits osteogenic differentiation by targeting bone morphogenetic protein-2
Abstract
Background and purpose: Trauma-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (TIONFH) is a major complication of femoral neck fractures. Degeneration and necrosis of subchondral bone can cause collapse, which results in hip joint dysfunction in patients. The destruction of bone metabolism homeostasis is an important factor for osteonecrosis. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have an important role in regulating osteogenic differentiation, but the mechanisms underlying abnormal bone metabolism of TIONFH are poorly understood. In this study, we screened specific miRNAs in TIONFH by microarray and further explored the mechanism of osteogenic differentiation.
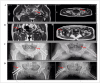
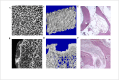
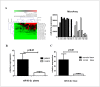
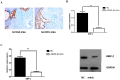
Design: Blood samples from patients with TIONFH and patients without necrosis after trauma were compared by microarray, and bone collapse of necrotic bone tissue was evaluated by micro-CT and immunohistochemistry. To confirm the relationship between miRNA and osteogenic differentiation, we conducted cell culture experiments. We found that many miRNAs were significantly different, including miR-93-5p; the increase in this miRNA was verified by Q-PCR. Comparison of the tissue samples showed that miR-93-5p expression increased, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and osteopontin (OPN) levels decreased, suggesting miR-93-5p may be involved in osteogenic differentiation. Further bioinformatics analysis indicated that miR-93-5p can target bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2). A luciferase gene reporter assay was performed to confirm these findings. By simulating and/or inhibiting miR-93-5p expression in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, we confirmed that osteogenic differentiation-related indictors, including BMP-2, Osterix, Runt-related transcription factor, ALP and OPN, were decreased by miR-93-5p.
Conclusion: Our study showed that increased miR-93-5p in TIONFH patients inhibited osteogenic differentiation, which may be associated with BMP-2 reduction. Therefore, miR-93-5p may be a potential target for prevention of TIONFH.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of miR-93-5p promotes osteogenic differentiation in a rabbit model of trauma-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head.FEBS Open Bio. 2021 Aug;11(8):2152-2165. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13218. Epub 2021 Jul 16. FEBS Open Bio. 2021. PMID: 34092046 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of micro RNA-335-5p regulating bone morphogenetic protein 2 on osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Jun 15;34(6):781-786. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201910097. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32538572 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
MicroRNA expression profiling of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells during osteogenic differentiation reveals Osterix regulation by miR-31.Gene. 2013 Sep 15;527(1):321-31. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.06.021. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23827457
-
Super-Enhancer-Associated Long Non-Coding RNA LINC01485 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Regulating MiR-619-5p/RUNX2 Axis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 19;13:846154. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.846154. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35663324 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circ_0000020 promotes osteogenic differentiation to reduce osteoporosis via sponging microRNA miR-142-5p to up-regulate Bone Morphogenetic Protein BMP2.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3824-3836. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1949514. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34266353 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MiR-93 inhibits the vascular calcification of chronic renal failure by suppression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Int Urol Nephrol. 2022 Jan;54(1):225-235. doi: 10.1007/s11255-021-02907-6. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Int Urol Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 34138419
-
The Regulation of Collagen Processing by miRNAs in Disease and Possible Implications for Bone Turnover.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 22;23(1):91. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010091. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircRNA_25487 inhibits bone repair in trauma-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head by sponging miR-134-3p through p21.Regen Ther. 2020 Dec 28;16:23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2020.12.003. eCollection 2021 Mar. Regen Ther. 2020. PMID: 33426239 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine-modified circCDK14 promotes ossification of the ligamentum flavum via epigenetic modulation by targeting AFF4.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Oct 16;81(1):436. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05460-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39414635 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-320a-5p contributes to the homeostasis of osteogenesis and adipogenesis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell.Regen Ther. 2022 Mar 28;20:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2022.03.001. eCollection 2022 Jun. Regen Ther. 2022. PMID: 35402661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu JF, Yang GH, Pan XH, Zhang SJ, Zhao C, Qiu BS, et al. Altered microRNA expression profile in exosomes during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2014; 9: e114627 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114627 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hwang S, Park SK, Lee HY, Kim SW, Lee JS, Choi EK, et al. miR-140-5p suppresses BMP2-mediated osteogenesis in undifferentiated human mesenchymal stem cells. FEBS Lett. 2014; 588: 2957–2963. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.05.048 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maes OC, An J, Sarojini H, Wang E. Murine microRNAs implicated in liver functions and aging process. Mech Ageing Dev. 2008; 129: 534–541. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2008.05.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Heo JS, Choi Y, Kim HS, Kim HO. Comparison of molecular profiles of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta and adipose tissue. Int J Mol Med. 2016; 37: 115–125. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2413 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brocher J, Janicki P, Voltz P, Seebach E, Neumann E, Mueller-Ladner U, et al. Inferior ectopic bone formation of mesenchymal stromal cells from adipose tissue compared to bone marrow: rescue by chondrogenic pre-induction. Stem Cell Res. 2013; 11: 1393–1406. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2013.07.008 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

