Polymorphisms of Plasmodium falciparum k13-propeller gene among migrant workers returning to Henan Province, China from Africa
- PMID: 28797235
- PMCID: PMC5553609
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-017-2634-z
Polymorphisms of Plasmodium falciparum k13-propeller gene among migrant workers returning to Henan Province, China from Africa
Abstract
Background: Henan Province has been in the malaria elimination stage, with all reports of the disease being imported since 2012 and over 90% coming from Africa. Surveillance and population studies are essential for the early detection and subsequent prevention of the spread of drug resistance. The K13-propeller gene was recently identified as a proposed molecular marker of artemisinin (ART) resistance. In this study, we detected mutations of the K13-propeller gene in samples taken from imported malaria cases in Henan Province from 2012 to 2015.
Methods: There were 483 samples that were obtained from Plasmodium falciparum-infected malaria migrant workers who returned to Henan Province from Africa between 2012 and 2015. The single nucleotide polymorphisms in the K13-propeller gene were assessed by nested PCR with DNA sequencing. Frequency and geographic difference of K13-propeller gene mutant types were analyzed.
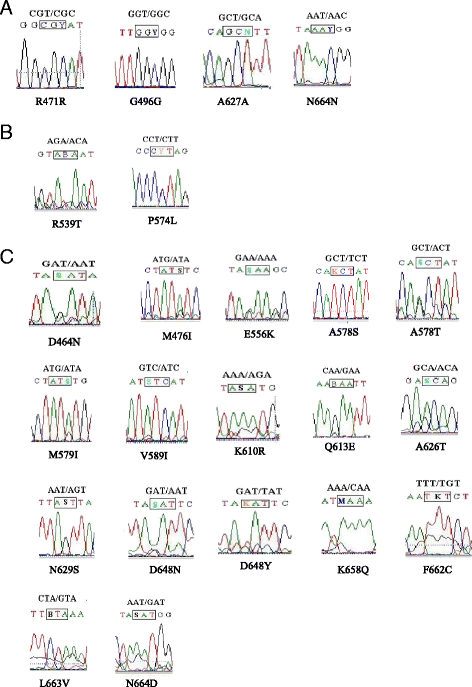
Results: Of 483 patients, 476 were cured and 7 died. There were no K13-propeller mutations in the blood samples from the 7 patients who died, but there were 23 different genotypes of the K13-propeller that were observed in 24 (4.97%) of the samples. C580Y, which was the predominant one in the resistance of ART, was not detected in the samples, but R539T and P574L which have also been associated with ART resistance, were observed in two samples from Angola and Equatorial Guinea. No mutations were detected in 11 samples from North Africa. The frequency of the K13-propeller was 6.50% (8/123) in Central Africa, followed by East Africa (1/19, 5.26%), West Africa (9/198, 4.55%) and South Africa (6/132, 4.55%). There was no significant difference among these four areas (P = 0.795).
Conclusion: R539T and P574L were found in migrant workers who traveled from Africa to Henan Province, although the frequency of the K13-propeller mutants was low. These data may enrich the molecular surveillance of antimalarial resistance and will be helpful for developing and updating the antimalarial policy in Henan Province.
Keywords: Africa; Artemisinin resistance; Henan Province; Imported malaria; K13-propeller gene; Plasmodium falciparum.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was reviewed and approved by the Project of Medical Science and Technique of Henan province (No. 201304053) and the Special Funding of the Henan Health Science and Technology Innovation Talent Project (No.4045). Before sampling, the purpose was illustrated to participants and consent was obtained from those who agreed to participate in the survey.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patients for the publication of this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
K13-propeller gene polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum parasite population in malaria affected countries: a systematic review of prevalence and risk factors.Malar J. 2019 Mar 7;18(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2701-6. Malar J. 2019. PMID: 30846002 Free PMC article.
-
K13-propeller gene polymorphisms of Plasmodium falciparum and the therapeutic effect of artesunate among migrant workers returning to Guangxi, China (2014-2017).Malar J. 2019 Oct 16;18(1):349. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2984-7. Malar J. 2019. PMID: 31619243 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular surveillance of Pfcrt and k13 propeller polymorphisms of imported Plasmodium falciparum cases to Zhejiang Province, China between 2016 and 2018.Malar J. 2020 Feb 4;19(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12936-020-3140-0. Malar J. 2020. PMID: 32019571 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms of pfcrt, pfmdr1, and K13-propeller genes in imported falciparum malaria isolates from Africa in Guizhou province, China.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Jul 16;20(1):513. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05228-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32677899 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on k13 mutant alleles for artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018 Apr;51(2):159-165. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2017.06.009. Epub 2017 Jun 29. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018. PMID: 28711439 Review.
Cited by
-
Malaria Risk and Prevention in Asian Migrants to Angola.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Nov;103(5):1918-1926. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-0706. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020. PMID: 32815500 Free PMC article.
-
Are k13 and plasmepsin II genes, involved in Plasmodium falciparum resistance to artemisinin derivatives and piperaquine in Southeast Asia, reliable to monitor resistance surveillance in Africa?Malar J. 2019 Aug 23;18(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2916-6. Malar J. 2019. PMID: 31443646 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of Pfk13 polymorphism in malaria patients treated with artemisinin-based therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Parasitol Res. 2024 May 14;123(5):209. doi: 10.1007/s00436-024-08203-3. Parasitol Res. 2024. PMID: 38740597
-
Molecular surveillance of putative drug resistance markers of antifolate and artemisinin among imported Plasmodium falciparum in Qatar.Pathog Glob Health. 2019 Jun;113(4):158-166. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2019.1639018. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Pathog Glob Health. 2019. PMID: 31296112 Free PMC article.
-
K13-propeller gene polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum parasite population in malaria affected countries: a systematic review of prevalence and risk factors.Malar J. 2019 Mar 7;18(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2701-6. Malar J. 2019. PMID: 30846002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . World malaria report. Geneva: WHO; 2016.
-
- Zhang HW, Su YP, Zhao XD, Yan QY, Liu Y, Chen JS. [Imported falciparum malaria situation in Henan Province during 2005-2009] (In chinese). Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2010;28: 476-477. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Guidelines for the treatment of malaria. Geneva: WHO; 2006.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

