Dual peptide-mediated targeted delivery of bioactive siRNAs to oral cancer cells in vivo
- PMID: 28797448
- PMCID: PMC5580030
- DOI: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.07.004
Dual peptide-mediated targeted delivery of bioactive siRNAs to oral cancer cells in vivo
Abstract
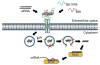
Objectives: Despite significant advances in cancer treatment, the prognosis for oral cancer remains poor in comparison to other cancer types, including breast, skin, and prostate. As a result, more effective therapeutic modalities are needed for the treatment of oral cancer. Consequently, in the present study, we examined the feasibility of using a dual peptide carrier approach, combining an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeting peptide with an endosome-disruptive peptide, to mediate targeted delivery of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) into EGFR-overexpressing oral cancer cells and induce silencing of the targeted oncogene, cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A).
Materials and methods: Fluorescence microscopy, real-time PCR, Western blot analysis, and in vivo bioimaging of mice containing orthotopic xenograft tumors were used to examine the ability of the dual peptide carrier to mediate specific delivery of bioactive siRNAs into EGFR-overexpressing oral cancer cells/tissues.
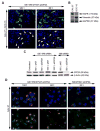
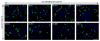
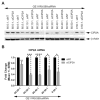
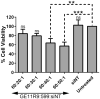
Results: Co-complexation of the EGFR-targeting peptide, GE11R9, with the endosome-disruptive 599 peptide facilitated the specific uptake of siRNAs into oral cancer cells overexpressing EGFR in vitro with optimal gene silencing observed at a 60:30:1 (GE11R9:599:siRNA) molar ratio. Furthermore, when administered systemically to mice bearing xenograft oral tumors, this dual peptide complex mediated increased targeted delivery of siRNAs into tumor tissues in comparison to the 599 peptide alone and significantly enhanced CIP2A silencing.
Conclusion: Herein we provide the first report demonstrating the clinical potential of a dual peptide strategy for siRNA-based therapeutics by synergistically mediating the effective targeting and delivery of bioactive siRNAs into EGFR-overexpressing oral cancer cells.
Keywords: CIP2A; Cell-penetrating; EGFR; Endosome-disruptive; Homing/targeting; OSCC; Oral cancer; Peptide; RNAi; siRNA.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fusogenic-oligoarginine peptide-mediated silencing of the CIP2A oncogene suppresses oral cancer tumor growth in vivo.J Control Release. 2015 Nov 28;218:72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.09.026. Epub 2015 Sep 18. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 26386438 Free PMC article.
-
Fusogenic-oligoarginine peptide-mediated delivery of siRNAs targeting the CIP2A oncogene into oral cancer cells.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 3;8(9):e73348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073348. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24019920 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference-mediated gene silencing of pleiotrophin through polyethylenimine-complexed small interfering RNAs in vivo exerts antitumoral effects in glioblastoma xenografts.Hum Gene Ther. 2006 Jul;17(7):751-66. doi: 10.1089/hum.2006.17.751. Hum Gene Ther. 2006. PMID: 16839274
-
Nanoparticles for targeted delivery of therapeutics and small interfering RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 14;21(42):12022-41. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12022. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26576089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyethylenimines for RNAi-mediated gene targeting in vivo and siRNA delivery to the lung.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011 Apr;77(3):438-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2010.11.007. Epub 2010 Nov 18. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011. PMID: 21093588 Review.
Cited by
-
Fusogenic peptide delivery of bioactive siRNAs targeting CSNK2A1 for treatment of ovarian cancer.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 Sep 19;30:95-111. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.09.012. eCollection 2022 Dec 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 36213692 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing peptide siRNA-carrier designs through L/D-amino acid stereochemical modifications to enhance gene silencing.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Mar 19;24:462-476. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.03.013. eCollection 2021 Jun 4. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 33868789 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced drug delivery systems for oral squamous cell carcinoma: a comprehensive review of nanotechnology-based and other innovative approaches.Front Drug Deliv. 2025 Jun 27;5:1596964. doi: 10.3389/fddev.2025.1596964. eCollection 2025. Front Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 40837711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs and Their Big Therapeutic Impacts: Delivery Strategies for Cancer Intervention.Cells. 2022 Jul 29;11(15):2332. doi: 10.3390/cells11152332. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35954176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNAs are Involved in the Process of Atherosclerosis at Diverse Levels.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022 Jun 10;118(6):1134-1140. doi: 10.36660/abc.20201383. eCollection 2022. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35703653 Free PMC article. Review. English, Portuguese.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359–86. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2017;67(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- ACS. Cancer Facts & Figures 2016. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2016.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

