Perivascular spaces, glymphatic dysfunction, and small vessel disease
- PMID: 28798076
- PMCID: PMC5567781
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20160381
Perivascular spaces, glymphatic dysfunction, and small vessel disease
Abstract
Cerebral small vessel diseases (SVDs) range broadly in etiology but share remarkably overlapping pathology. Features of SVD including enlarged perivascular spaces (EPVS) and formation of abluminal protein deposits cannot be completely explained by the putative pathophysiology. The recently discovered glymphatic system provides a new perspective to potentially address these gaps. This work provides a comprehensive review of the known factors that regulate glymphatic function and the disease mechanisms underlying glymphatic impairment emphasizing the role that aquaporin-4 (AQP4)-lined perivascular spaces (PVSs), cerebrovascular pulsatility, and metabolite clearance play in normal CNS physiology. This review also discusses the implications that glymphatic impairment may have on SVD inception and progression with the aim of exploring novel therapeutic targets and highlighting the key questions that remain to be answered.
Keywords: CNS clearance; Cerebrospinal fluid; Glymphatic; Perivascular space; Small vessel disease.
© 2017 The Author(s). Published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
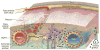
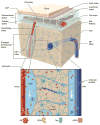
References
-
- Hachinski V World Stroke O. Stroke and Potentially Preventable Dementias Proclamation: Updated World Stroke Day Proclamation. Stroke. 2015;46(11):3039–40. - PubMed
-
- Charidimou A, Pantoni L, Love S. The concept of sporadic cerebral small vessel disease: A road map on key definitions and current concepts. Int J Stroke. 2016;11(1):6–18. - PubMed
-
- Pantoni L. Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9(7):689–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

