Enrofloxacin and Toltrazuril Are Able to Reduce Toxoplasma gondii Growth in Human BeWo Trophoblastic Cells and Villous Explants from Human Third Trimester Pregnancy
- PMID: 28798905
- PMCID: PMC5526852
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00340
Enrofloxacin and Toltrazuril Are Able to Reduce Toxoplasma gondii Growth in Human BeWo Trophoblastic Cells and Villous Explants from Human Third Trimester Pregnancy
Abstract
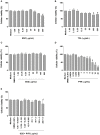
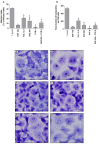
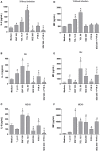
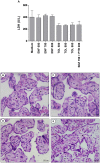
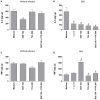
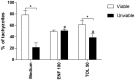
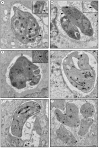
Classical treatment for congenital toxoplasmosis is based on combination of sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine plus folinic acid. Due to teratogenic effects and bone marrow suppression caused by pyrimethamine, the establishment of new therapeutic strategies is indispensable to minimize the side effects and improve the control of infection. Previous studies demonstrated that enrofloxacin and toltrazuril reduced the incidence of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii infection. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy of enrofloxacin and toltrazuril in the control of T. gondii infection in human trophoblast cells (BeWo line) and in human villous explants from the third trimester. BeWo cells and villous were treated with several concentrations of enrofloxacin, toltrazuril, sulfadiazine, pyrimethamine, or combination of sulfadiazine+pyrimethamine, and the cellular or tissue viability was verified. Next, BeWo cells were infected by T. gondii (2F1 clone or the ME49 strain), whereas villous samples were only infected by the 2F1 clone. Then, infected cells and villous were treated with all antibiotics and the T. gondii intracellular proliferation as well as the cytokine production were analyzed. Finally, we evaluated the direct effect of enrofloxacin and toltrazuril in tachyzoites to verify possible changes in parasite structure. Enrofloxacin and toltrazuril did not decrease the viability of cells and villous in lower concentrations. Both drugs were able to significantly reduce the parasite intracellular proliferation in BeWo cells and villous explants when compared to untreated conditions. Regardless of the T. gondii strain, BeWo cells infected and treated with enrofloxacin or toltrazuril induced high levels of IL-6 and MIF. In villous explants, enrofloxacin induced high MIF production. Finally, the drugs increased the number of unviable parasites and triggered damage to tachyzoite structure. Taken together, it can be concluded that enrofloxacin and toltrazuril are able to control T. gondii infection in BeWo cells and villous explants, probably by a direct action on the host cells and parasites, which leads to modifications of cytokine release and tachyzoite structure.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii; enrofloxacin; placenta; toltrazuril; treatment; trophoblast.
Figures


References
-
- Angeloni M. B., Guirelli P. M., Franco P. S., Barbosa B. F., Gomes A. O., Castro A. S., et al. (2013). Differential apoptosis in BeWo cells after infection with highly (RH) or moderately (ME49) virulent strains of Toxoplasma gondii is related to the cytokine profile secreted, the death receptor Fas expression and phosphorylated ERK1/2 expression. Placenta 34, 973–982. 10.1016/j.placenta.2013.09.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barbosa B. F., Lopes-Maria J. B., Gomes A. O., Angeloni M. B., Castro A. S., Franco P. S., et al. (2015). IL10, TGF beta1, and IFN gamma modulate intracellular signaling pathways and cytokine production to control Toxoplasma gondii infection in BeWo trophoblast cells. Biol. Reprod. 92, 1–13. 10.1095/biolreprod.114.124115 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

