Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Protect Rat Corneal Epithelial Cells against Ultraviolet B-Induced Apoptosis by Attenuating the Mitochondrial Pathway and Inhibiting JNK Phosphorylation
- PMID: 28798932
- PMCID: PMC5536140
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/5806832
Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Protect Rat Corneal Epithelial Cells against Ultraviolet B-Induced Apoptosis by Attenuating the Mitochondrial Pathway and Inhibiting JNK Phosphorylation
Abstract
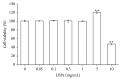
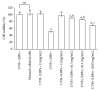
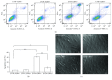
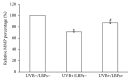
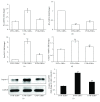
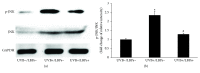
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides (LBPs) have been shown to play a key role in protecting the eyes by reducing the apoptosis induced by certain types of damage. However, it is not known whether LBPs can protect damaged corneal cells from apoptosis. Moreover, no reports have focused on the role of LBPs in guarding against ultraviolet B- (UVB-) induced apoptosis. The present study aimed to investigate the protective effect and underlying mechanism of LBPs against UVB-induced apoptosis in rat corneal epithelial (RCE) cells. The results showed that LBPs significantly prevented the loss of cell viability and inhibited cell apoptosis induced by UVB in RCE cells. LBPs also inhibited UVB-induced loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, downregulation of Bcl-2, and upregulation of Bax and caspase-3. Finally, LBPs attenuated the phosphorylation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) triggered by UVB. In summary, LBPs protect RCE cells against UVB-induced damage and apoptosis, and the underlying mechanism involves the attenuation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway and the inhibition of JNK phosphorylation.
Figures

References
-
- Kolozsvari L., Nogradi A., Hopp B., Bor Z. UV absorbance of the human cornea in the 240- to 400-nm range. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2002;43(7):2165–2168. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

