Transient Descending Colocolonic Intussusception Due to a Large Fecaloma in an Adult
- PMID: 28798942
- PMCID: PMC5541757
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.2017.94
Transient Descending Colocolonic Intussusception Due to a Large Fecaloma in an Adult
Abstract
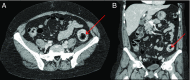
Intussusception typically occurs in infants and children, with adults representing 5% of cases. A 53-year-old African American woman presented with lower abdominal pain and tenderness. Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrated a 3.5 cm colocolonic intussusception in the descending colon. Emergent colonoscopy found solid stool in the mid descending colon. Water-soluble rectal enema showed a filling defect in the mid descending colon. Repeat colonoscopy demonstrated presence of a large fecaloma in left colon. Laxatives were initiated, and abdominal pain subsided. To our knowledge, this is the first report of colocolonic intussusception secondary to fecaloma.
Figures


References
-
- Weilbaecher D, Bolin JA, Hearn D, Ogden W. Intussusception in adults. Review of 160 cases. Am J Surg. 1971;121:531–5. - PubMed
-
- Agha FP. Intussusception in adults. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986;146:527–31. - PubMed
-
- Knowles MC, Fishman EK, Kuhlman JE, Bayless TM. Transient intussusception in Crohn disease: CT evaluation. Radiology. 1989;170:814.. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

