Single-dose botulinum toxin type a compared with repeated-dose for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: a pilot study
- PMID: 28799056
- PMCID: PMC5552618
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-017-0793-3
Single-dose botulinum toxin type a compared with repeated-dose for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Several RCT studies including ours, seem to prove the role of Botulinum toxin type A (BTX-A) in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia (TN), but no standardized dosing regimen has been established. In our study, we compare two different methods of administration: single-dose or repeated-dose strategy which was most frequently applied over the years in our centre.
Methods: An open-label trail was conducted. One hundred patients with classic TN symptoms were recruited, and randomly and equally apportioned to single- or repeated-dose group. Patients in the single-dose group received a local BTX-A injection of 70 to 100 U. The repeated-dose group received an initial BTX-A injection of 50 to 70 U and then another of equal volume 2 weeks later. All patients were followed for 6 months.
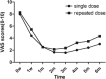
Results: In the single- and repeated-dose groups, 44 and 37, respectively, completed the entire study. The groups were statistically similar in TN frequency, time between treatment and effect, time to peak effect, VAS scores, and rates of adverse reactions (latency and duration). However, the single-dose group experienced significantly longer duration of effect (P = 0.032).
Conclusions: The single- and repeated-dosing BTX-A regimens were largely comparable in efficacy and safety. This study suggests that repeated dosing has no advantage over single dosing of BTX-A for TN. Dosing should be adjusted for the individual patient.
Keywords: Botulinum toxin type a; Repeated dosing; Single dosing; Trigeminal neuralgia.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Botulinum Toxin Type A for Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Comprehensive Literature Review.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Nov 20;16(11):500. doi: 10.3390/toxins16110500. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Botulinum neurotoxin type A in the treatment of classical Trigeminal Neuralgia (BoTN): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2015 Dec 3;16:550. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-1052-z. Trials. 2015. PMID: 26634453 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Two doses of botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: observation of therapeutic effect from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.J Headache Pain. 2014 Sep 27;15(1):65. doi: 10.1186/1129-2377-15-65. J Headache Pain. 2014. PMID: 25263254 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Liquid-type Botulinum Toxin Type A in Adductor Spasmodic Dysphonia: A Prospective Pilot Study.J Voice. 2017 May;31(3):378.e19-378.e24. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Aug 9. J Voice. 2017. PMID: 27520509
-
Topical Review: Potential Use of Botulinum Toxin in the Management of Painful Posttraumatic Trigeminal Neuropathy.J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2017 Winter;31(1):7-18. doi: 10.11607/ofph.1753. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2017. PMID: 28118416 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Botulinum Toxin Injection on EMG Activity and Bite Force in Masticatory Muscle Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Aug 10;14(8):545. doi: 10.3390/toxins14080545. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36006207 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Compared to oxcarbazepine and carbamazepine, botulinum toxin type A is a useful therapeutic option for trigeminal neuralgia symptoms: A systematic review.Clin Exp Dent Res. 2024 Apr;10(2):e882. doi: 10.1002/cre2.882. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2024. PMID: 38558383 Free PMC article.
-
Botulinum Neurotoxin for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain.Front Neurol. 2020 Aug 11;11:716. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00716. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32849195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Botulinum Toxin Type A for Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Comprehensive Literature Review.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Nov 20;16(11):500. doi: 10.3390/toxins16110500. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lantox-The Chinese Botulinum Toxin Drug-Complete English Bibliography and Comprehensive Formalised Literature Review.Toxins (Basel). 2021 May 22;13(6):370. doi: 10.3390/toxins13060370. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu CJ, Shen JH, Chen Y, Lian YJ. Comparison of two different formulations of botulinum toxin a for the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. Turk Neurosurg. 2011;21(4):625–629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical