Suboptimal cotrimoxazole prophylactic concentrations in HIV-infected children according to the WHO guidelines
- PMID: 28800382
- PMCID: PMC5698578
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13397
Suboptimal cotrimoxazole prophylactic concentrations in HIV-infected children according to the WHO guidelines
Abstract
Aims: A clinical study was conduct in HIV-infected children to evaluate the prophylactic doses of cotrimoxazole [sulfamethoxazole (SMX) and trimethoprim (TMP)] advised by the WHO.
Methods: Children received lopinavir-based antiretroviral therapy with cotrimoxazole prophylaxis (200 mg of SMX/40 mg of TMP once daily). A nonlinear mixed effects modelling approach was used to analyse plasma concentrations. Factors that could impact the pharmacokinetic profile were investigated. The model was subsequently used to simulate individual exposure and evaluate different administration schemes.
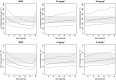
Results: The cohort comprised 136 children [average age: 1.9 years (range: [0.7-4]), average weight: 9.5 kg (range: [6-16.3])]. A dose per kg was justified by the significant influence of implementing an allometrically scaled body size covariate on SMX and TMP pharmacokinetics. SMX and TPM clearance were estimated at 0.49 l h-1 /9.5 kg and 3.06 l h-1 /9.5 kg, respectively. The simulated exposures obtained after administration of oral dosing recommended by the WHO for children from 10 to 15 kg were significantly lower than in adults for SMX and TMP. This could induce a reduction of effectiveness of cotrimoxazole. Simulations show that regimens of 30 mg kg-1 of SMX and 6 mg kg-1 of TMP in the 5-10 kg group and 25 mg kg-1 of SMX and 5 mg kg-1 of TMP in the 10-15 kg group are more suitable doses.
Conclusions: In this context of high prevalence of opportunistic infections, a lower exposure to cotrimoxazole in children than adults was noted. To achieve comparable exposure to adults, a dosing scheme per kg was proposed.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01127204.
Keywords: HIV; children; pharmacokinetics; sulfamethoxazole; trimethoprim.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Newell M‐L, Brahmbhatt H, Ghys PD. Child mortality and HIV infection in Africa: a review. AIDS Lond Engl 2004; 18 (Suppl 2): S27–S34. - PubMed
-
- Newell M‐L, Coovadia H, Cortina‐Borja M, Rollins N, Gaillard P, Dabis F, et al, Ghent International AIDS Society (IAS) Working Group on HIV Infection in Women and Children . Mortality of infected and uninfected infants born to HIV‐infected mothers in Africa: a pooled analysis. Lancet Lond Engl 2004; 364: 1236–1243. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organisation . Guideline on when to start antiretroviral therapy and on pre‐exposure prophylaxis for HIV. Geneva: WHO; 2015 [updated 30 September 2015]. Available at http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/186275/1/9789241509565_eng.pdf?.... - PubMed
-
- Valdez H, Chowdhry TK, Asaad R, Woolley IJ, Davis T, Davidson R, et al Changing spectrum of mortality due to human immunodeficiency virus: analysis of 260 deaths during 1995–1999. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am 2001; 32: 1487–1493. - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS . Report on the global HIV/AIDS epidemic – June 2000. Use of cotrimoxazole prophylaxis in people with HIV/AIDS in Africa.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

