Targeting lysyl oxidase reduces peritoneal fibrosis
- PMID: 28800626
- PMCID: PMC5553776
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183013
Targeting lysyl oxidase reduces peritoneal fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Abdominal surgery and disease cause persistent abdominal adhesions, pelvic pain, infertility and occasionally, bowel obstruction. Current treatments are ineffective and the aetiology is unclear, although excessive collagen deposition is a consistent feature. Lysyl oxidase (Lox) is a key enzyme required for crosslinking and deposition of insoluble collagen, so we investigated whether targeting Lox might be an approach to reduce abdominal adhesions.
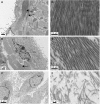
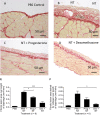
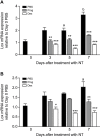
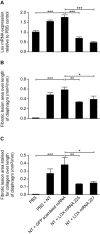
Methods: Female C57Bl/6 mice were treated intraperitoneally with multiwalled carbon nanotubes (NT) to induce fibrosis, together with chemical (ß-aminoproprionitrile-BAPN) or miRNA Lox inhibitors, progesterone or dexamethasone. Fibrotic lesions on the diaphragm, and expression of fibrosis-related genes in abdominal wall peritoneal mesothelial cells (PMC) were measured. Effects of BAPN and dexamethasone on collagen fibre alignment were observed by TEM. Isolated PMC were cultured with interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1α) and progesterone to determine effects on Lox mRNA in vitro.
Results: NT-induced fibrosis and collagen deposition on the diaphragm was ameliorated by BAPN, Lox miRNA, or steroids. BAPN and dexamethasone disrupted collagen fibres. NT increased PMC Lox, Col1a1, Col3a1 and Bmp1 mRNA, which was inhibited by steroids. Progesterone significantly inhibited IL-1α induced Lox expression by PMC in vitro.
Conclusion: Our results provide proof-of-concept that targeting peritoneal Lox could be an effective approach in ameliorating fibrosis and adhesion development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Vercellini P, Viganò P, Somigliana E, Fedele L. Endometriosis: pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10: 261–275. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2013.255 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pados G, Venetis CA, Almaloglou K, Tarlatzis BC. Prevention of intra-peritoneal adhesions in gynaecological surgery: theory and evidence. Reprod Biomed Online. 2010; 21: 290–293. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2010.04.021 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmad G, Mackie FL, Iles DA, O’Flynn H, Dias S, Metwally M. et al. Fluid and pharmacological agents for adhesion prevention after gynaecological surgery. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2014; Issue 7, Art No: CD001298. - PubMed
-
- Jansen RP. Controlled clinical approaches to investigating the prevention of peritoneal adhesions. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;358: 177–192. - PubMed
-
- Fayez JA, Schneider PJ. Prevention of pelvic adhesion formation by different modalities of treatment. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987;157: 1184–1186. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

