A type I combi-targeting approach for the design of molecules with enhanced potency against BRCA1/2 mutant- and O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (mgmt)- expressing tumour cells
- PMID: 28800752
- PMCID: PMC5553999
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3504-1
A type I combi-targeting approach for the design of molecules with enhanced potency against BRCA1/2 mutant- and O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (mgmt)- expressing tumour cells
Abstract
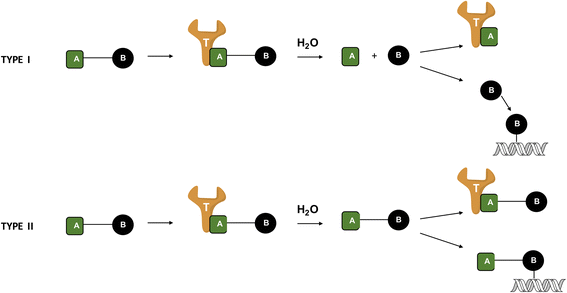
Background: Mutations of the DNA repair proteins BRCA1/2 are synthetically lethal with the DNA repair enzyme poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), which when inhibited, leads to cell death due to the absence of compensatory DNA repair mechanism. The potency of PARP inhibitors has now been clinically proven. However, disappointingly, acquired resistance mediated by the reactivation of wild type BRCA1/2 has been reported. In order to improve their efficacy, trials are ongoing to explore their combinations with temozolomide (TMZ). Here, in order to enhance potency in BRCA1/2-mutant cells, we report on the design of single molecules termed "combi-molecules" capable of not only inhibiting PARP but also damaging DNA like TMZ, which is known to induce a large number of DNA adducts. The majority of these lesions are processed through PARP-dependent base-excision repair machinery. Paradoxically, the least abundant lesion, the O6-methylguanine adduct is the most cytotoxic. Its repair by the O6-methylguanine DNA methyl transferase (MGMT) confers robust resistance to TMZ. Thus, we surmise that a combi-molecule designed to generate the same DNA adducts as TMZ, with an additional ability to block PARP, could induce BRCA1/2 mutant selective potency and a growth inhibitory profile independent of MGMT status.
Methods: The hydrolysis of EG22 and its stabilized form ZSM02 was analyzed by HPLC and fluorescence spectroscopy. Growth inhibitory potency was determined by SRB assay. PARP inhibition was determined by an enzyme assay and DNA damage by the comet assay. Subcellular distribution was visualized by confocal microscopy.
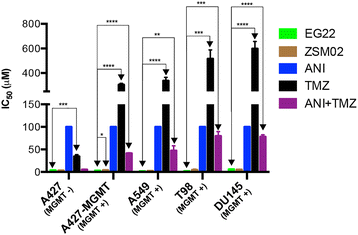
Results: Studies on EG22 showed that: (a) it inflicted anomalously higher levels of DNA damage than TMZ (b) it induced PARP inhibitory potency in the same range as ANI, a known PARP inhibitor (IC50 = 0.10 μM) (c) it showed strong potency in both BRCA1/2 wild type and mutated cells with 6-fold selectivity for the mutants and it was 65-303-fold more potent than TMZ and 4-63-fold than ANI alone and 3-47-fold than their corresponding equimolar combinations and (d) its potency was independent of MGMT expression.
Conclusion: The results in toto suggest that a combi-molecular approach directed at blocking PARP and damaging DNA can lead to single molecules with selective and enhanced potency against BRCA1/2 mutant and with activity independent of MGMT, the major predictive biomarker for resistance to TMZ.
Keywords: 1,2,3-methyltriazene; BRCA1/2 reactivation; Chemoresistance; Combi-targeting; DNA repair; MGMT; PARP inhibitor; Temozolomide.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics approval was not required for the use of human cell lines in this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures








References
-
- Sultana R, McNeill DR, Abbotts R, Mohammed MZ, Zdzienicka MZ, Qutob H, Seedhouse C, Laughton CA, Fischer PM, Patel PM, et al. Synthetic lethal targeting of DNA double-strand break repair deficient cells by human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease inhibitors. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(10):2433–2444. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27512. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Audeh MW, Carmichael J, Penson RT, Friedlander M, Powell B, Bellmcguinn KM, Scott C, Weitzel JN, Oaknin A, Loman N, et al. Oral poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor olaparib in patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations and recurrent ovarian cancer: a proof-of-concept trial. Lancet. 376(9737):245–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

