Anthelminthic properties of Methylene chloride-methanol (1:1) extracts of two Cameroonians medicinal plants on Heligmosomoides bakeri (Nematoda: Heligmosomatidea)
- PMID: 28800757
- PMCID: PMC5553925
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1908-8
Anthelminthic properties of Methylene chloride-methanol (1:1) extracts of two Cameroonians medicinal plants on Heligmosomoides bakeri (Nematoda: Heligmosomatidea)
Abstract
Background: The resistance of some medico-veterinary parasite strains as well as the unavailability and toxicity of synthetic anthelminthics on humans, animals and the impacts of their residues in the environment have pushed scientists to turn to plants with anthelminthic properties. Hence, the aim of this work was to contribute to the fight against helminths of medical and veterinary importance in general, and also to clear the environment of their free living stages.
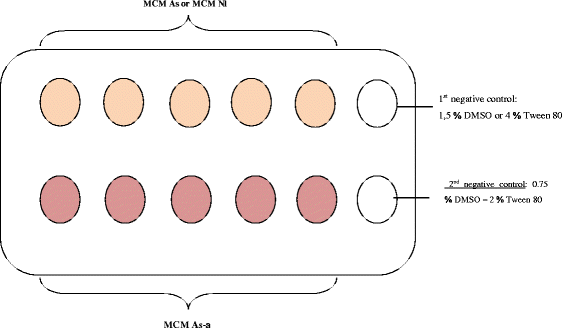
Methods: Fresh eggs of Heligmosomoides bakeri were obtained from the faeces of experimentally infected mice. L1 and L2 larval stages were obtained after 48 and 72 h of coproculture respectively. Methylene Chloride-Methanol (1:1) extracts of Annona senegalensis and Nauclea latifolia were diluted in DMSO or Tween 80 to prepare the following concentrations: 625, 1250, 2500, 3750 and 5000 μg/ml. The effects of extract solutions were evaluated on the embryonation of eggs, egg hatching and on L1 and L2 survival after 48, 10 and 24 h of incubation. Negative controls were 1.5% DMSO, 4% Tween 80 and a mixture of these solvents. The TLC was carried out and the profiles of secondary metabolites were made.
Results: Negative controls had no effect on the embryonation, eggs hatching and on larval mortality. However, it was found that, the extracts affected the free living stages of H. bakeri in a concentration-dependant manner. At the highest concentration (5000 μg/ml), the rate of inhibition of embryonation obtained were 20.80%, 38.15% and 84.83% for Methylene Chloride-Methanol of Annona senegalensis (MCM As), Nauclea latifolia (MCM Nl) extracts and mixture of Annona senegalensis and Nauclea latifolia (MCM As-Nl) extract respectively. For egg hatch, the inhibition rate was 16.10%, 46.24% and 87.07% for the above three extracts respectively at the same concentration of 5000 μg/ml. On L1 and L2 larval stages after 24 h of exposure to extracts, the mortality rates of 100%, 54.76% and 96.77% against 98%, 51.44% and 100% were obtained for MCM As, MCM Nl and MCM As-Nl respectively at the highest concentration. The Methylene Chloride-Methanol of A.senegalensis, N. latifolia extracts showed the presence of alkaloids except in N. latifolia extract, flavonoids, sterols, triterpens, tanins, polyphenols, anthraquinons, saponins and terpenoids.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that, the mixture of the two plant extracts showed an additive (synergetic effect) ovicidal effect and a slight larval mortality on L1 as compared to the effect of MCM As extract alone. These effects were due to the presence ao secondary metabolites identifies in the plant extracts. Thus, they may be used as possible «disinfectants» for soil transmitted nematodes.
Keywords: Additive effect; Annona senegalensis; Heligmosomoides bakeri; Nauclea latifolia.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
Experimental protocols used in this study were approved by the Research Unit of Biology and Applied Ecology committee, Department of Animal Biology, University of Dschang, Cameroon.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro nematicidal activity of extracts of Canthium mannii (Rubiaceae), on different life-cycle stages of Heligmosomoides polygyrus (Nematoda, Heligmosomatidae).J Helminthol. 2010 Jun;84(2):156-65. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X09990435. Epub 2009 Sep 4. J Helminthol. 2010. PMID: 19728896
-
In vitro anthelminthic efficacy of Dichrocephala integrifolia (Asteraceae) extracts on the gastro-intestinal nematode parasite of mice: Heligmosomoides bakeri (Nematoda, Heligmosomatidae).Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2013 Feb;3(2):100-4. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(13)60032-5. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2013. PMID: 23593587 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of different extracts of three Annona species on egg-hatching processes of Haemonchus contortus.J Helminthol. 2019 Aug 28;94:e77. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X19000397. J Helminthol. 2019. PMID: 31455460
-
Traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties of African Nauclea species: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Feb 15;212:106-136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.011. Epub 2017 Oct 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29045823 Review.
-
Anthelmintic activity of plants against gastrointestinal nematodes of goats: a review.Parasitology. 2019 Sep;146(10):1233-1246. doi: 10.1017/S0031182019000672. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Parasitology. 2019. PMID: 31104640
Cited by
-
Anthelmintic Activity of Ethanolic and Aqueous Extracts of Khaya grandifoliola Stem Bark against Heligmosomoides polygyrus: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches.J Trop Med. 2024 Jul 17;2024:6735764. doi: 10.1155/2024/6735764. eCollection 2024. J Trop Med. 2024. PMID: 39050406 Free PMC article.
-
Nematocidal Activity of Ethanol and Aqueous Extracts of Persea americana Seeds against Heligmosomoides polygyrus using the Worm Microtracker Method.J Parasitol Res. 2023 Sep 14;2023:9545565. doi: 10.1155/2023/9545565. eCollection 2023. J Parasitol Res. 2023. PMID: 37745983 Free PMC article.
-
Antihelminthic Activity of Lophira Lanceolata on Heligmosomoides polygyrus Using an Automated High-Throughput Method.J Trop Med. 2023 Jan 20;2023:9504296. doi: 10.1155/2023/9504296. eCollection 2023. J Trop Med. 2023. PMID: 36713298 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Silico Anthelmintic Activity of Extracts of Lannea kerstingii and Ficus thonningii on Heligmosomoides polygyrus.J Parasitol Res. 2024 Aug 3;2024:1858154. doi: 10.1155/2024/1858154. eCollection 2024. J Parasitol Res. 2024. PMID: 39131749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Etung kollins N, Wabo Pone J, Payne VK, Yondo J, Komtangi MC, Mpoame Mbida, Bilong Bilong, C. In vitro Comparative effect of aqueous (cold and hot water) and ethanolic extracts of the seeds of aframomum danielli (zingiberaceae) on three life cycle stages of the parasitic nematode Heligmosomoides Bakeri (Nematoda; Heligmosomatidae), parasite of the laboratory mice (Mus Musculus). Med Aromat Plants. 2012;1:111. doi: 10.4172/2167-0412.1000111.
-
- Nandhini A, Sumathi C. An overview of herbals used in helminthosis. World J Pharm Res. 2014;3(10):350–362.
-
- WHO. Link between water and rehabilitation, health and hygiene: figure and accomplished facts. Geneva. 2004. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/facts2004/en/.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

