IL-4/IL-13 Heteroreceptor Influences Th17 Cell Conversion and Sensitivity to Regulatory T Cell Suppression To Restrain Experimental Allergic Encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 28801358
- PMCID: PMC5605454
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700372
IL-4/IL-13 Heteroreceptor Influences Th17 Cell Conversion and Sensitivity to Regulatory T Cell Suppression To Restrain Experimental Allergic Encephalomyelitis
Abstract
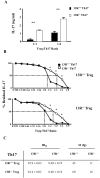
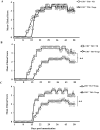
IL-4 and IL-13 have been defined as anti-inflammatory cytokines that can counter myelin-reactive T cells and modulate experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. However, it is not known whether endogenous IL-4 and IL-13 contribute to the maintenance of peripheral tolerance and whether their function is coordinated with T regulatory cells (Tregs). In this study, we used mice in which the common cytokine receptor for IL-4 and IL-13, namely the IL-4Rα/IL-13Rα1 (13R) heteroreceptor (HR), is compromised and determined whether the lack of signaling by endogenous IL-4 and IL-13 through the HR influences the function of effector Th1 and Th17 cells in a Treg-dependent fashion. The findings indicate that mice-deficient for the HR (13R-/-) are more susceptible to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis than mice sufficient for the HR (13R+/+) and develop early onset and more severe disease. Moreover, Th17 cells from 13R-/- mice had reduced ability to convert to Th1 cells and displayed reduced sensitivity to suppression by Tregs relative to Th17 effectors from 13R+/+ mice. These observations suggest that IL-4 and IL-13 likely operate through the HR and influence Th17 cells to convert to Th1 cells and to acquire increased sensitivity to suppression, leading to control of immune-mediated CNS inflammation. These previously unrecognized findings shed light on the intricacies underlying the contribution of cytokines to peripheral tolerance and control of autoimmunity.
Copyright © 2017 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures






References
-
- Miller JF, Morahan G. Peripheral T cell tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:51–69. - PubMed
-
- Garren H, Ruiz PJ, Watkins TA, Fontoura P, Nguyen LT, Estline ER, Hirschberg DL, Steinman L. Combination of gene delivery and DNA vaccination to protect from and reverse Th1 autoimmune disease via deviation to the Th2 pathway. Immunity. 2001;15:15–22. - PubMed
-
- Cash E, Minty A, Ferrara P, Caput D, Fradelizi D, Rott O. Macrophage-inactivating IL-13 suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rats. J Immunol. 1994;153:4258–4267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

