Protein glutaminylation is a yeast-specific posttranslational modification of elongation factor 1A
- PMID: 28801462
- PMCID: PMC5625034
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.801035
Protein glutaminylation is a yeast-specific posttranslational modification of elongation factor 1A
Abstract
Ribosomal translation factors are fundamental for protein synthesis and highly conserved in all kingdoms of life. The essential eukaryotic elongation factor 1A (eEF1A) delivers aminoacyl tRNAs to the A-site of the translating 80S ribosome. Several studies have revealed that eEF1A is posttranslationally modified. Using MS analysis, site-directed mutagenesis, and X-ray structural data analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae eEF1A, we identified a posttranslational modification in which the α amino group of mono-l-glutamine is covalently linked to the side chain of glutamate 45 in eEF1A. The MS analysis suggested that all eEF1A molecules are modified by this glutaminylation and that this posttranslational modification occurs at all stages of yeast growth. The mutational studies revealed that this glutaminylation is not essential for the normal functions of eEF1A in S. cerevisiae However, eEF1A glutaminylation slightly reduced growth under antibiotic-induced translational stress conditions. Moreover, we identified the same posttranslational modification in eEF1A from Schizosaccharomyces pombe but not in various other eukaryotic organisms tested despite strict conservation of the Glu45 residue among these organisms. We therefore conclude that eEF1A glutaminylation is a yeast-specific posttranslational modification that appears to influence protein translation.
Keywords: GTPase; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Schizosaccharomyces pombe; eukaryotic elongation factor eEF1A; glutaminylation; helix A*–loop–helix A′ region; posttranslational modification (PTM); protein synthesis; switch I region; translation elongation factor.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


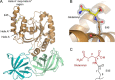


References
-
- Andersen G. R., Nissen P., and Nyborg J. (2003) Elongation factors in protein biosynthesis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28, 434–441 - PubMed
-
- Lamberti A., Caraglia M., Longo O., Marra M., Abbruzzese A., and Arcari P. (2004) The translation elongation factor 1A in tumorigenesis, signal transduction and apoptosis: review article. Amino Acids 26, 443–448 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

