Assessment of imatinib as first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia: 10-year survival results of the randomized CML study IV and impact of non-CML determinants
- PMID: 28804124
- PMCID: PMC5668495
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2017.253
Assessment of imatinib as first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia: 10-year survival results of the randomized CML study IV and impact of non-CML determinants
Abstract
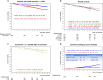
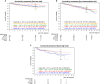
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)-study IV was designed to explore whether treatment with imatinib (IM) at 400 mg/day (n=400) could be optimized by doubling the dose (n=420), adding interferon (IFN) (n=430) or cytarabine (n=158) or using IM after IFN-failure (n=128). From July 2002 to March 2012, 1551 newly diagnosed patients in chronic phase were randomized into a 5-arm study. The study was powered to detect a survival difference of 5% at 5 years. After a median observation time of 9.5 years, 10-year overall survival was 82%, 10-year progression-free survival was 80% and 10-year relative survival was 92%. Survival between IM400 mg and any experimental arm was not different. In a multivariate analysis, risk group, major-route chromosomal aberrations, comorbidities, smoking and treatment center (academic vs other) influenced survival significantly, but not any form of treatment optimization. Patients reaching the molecular response milestones at 3, 6 and 12 months had a significant survival advantage. For responders, monotherapy with IM400 mg provides a close to normal life expectancy independent of the time to response. Survival is more determined by patients' and disease factors than by initial treatment selection. Although improvements are also needed for refractory disease, more life-time can currently be gained by carefully addressing non-CML determinants of survival.
Conflict of interest statement
RH received research support from Novartis and honoraria from BMS, SS research support from Novartis, BMS, Ariad and Pfizer, MP honoraria from Novartis and BMS, SK honoraria from Novartis, GMB honoraria from Novartis, BMS and Pfizer, THB research support from Novartis, MCM grants and honoraria from Novartis, BMS, Ariad and Pfizer, AB honoraria from BMS, JM research support from Novartis and BMS, HL honoraria from Novartis, PS honoraria from Novartis, BMS, Pfizer and Ariad, CS honoraria from Novartis, AH research support from Novartis and honoraria from Novartis, BMS and Pfizer; all other authors reported no conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Precision tyrosine kinase inhibitor dosing in chronic myeloid leukemia?Haematologica. 2019 May;104(5):862-864. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.214445. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 31040230 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- O'Brien S, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 994–1004. - PubMed
-
- Hehlmann R, Lauseker M, Jung-Munkwitz S, Leitner A, Mueller MC, Pletsch N et al. Tolerability-adapted imatinib 800mg/d versus 400mg/d versus 400mg/d plus interferon-alpha in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 1634–1642. - PubMed
-
- Hanfstein B, Müller MC, Hehlmann R, Erben P, Lauseker M, Fabarius A et al. Early molecular and cytogenetic response is predictive for long-term progression-free and overall survival in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Leukemia 2012; 26: 2096–2102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

