[Reliability and validity of Turkish translation of the pediatric sleep questionnaire]
- PMID: 28804251
- PMCID: PMC5551494
[Reliability and validity of Turkish translation of the pediatric sleep questionnaire]
Abstract
Objective: Aim of this study was to investigate the validity and reliability of the Turkish translation of Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire (PSQ)-the extended version. The Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire (PSQ) has two versions: a shorter one, which has been validated for sleep-related breathing disorders, and an extended version, which deals with a wider range of sleep disturbances.
Method: After translation and back-translation of the PSQ, it was filled in by the parents of 99 patients with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), 34 patients with Upper Airway Resistance and Snoring (UARS), and 42 healthy controls. Cronbach alpha was computed as a measure of internal consistency along with test-retest reliability and item-total score correlations. We used principal components analysis and varimax rotation to investigate the factor structure. The Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC) curves were used to determine cut-off points, sensitivity, specificity, and negative and positive predictive values.
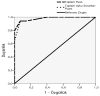
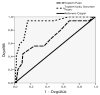
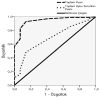
Results: Cronbach alpha coefficient was 0.77 for the whole questionnaire. Similar to the original PSQ study, we found four factors, namely "Snoring," "Behavioral Problems," "Breathing Problems," and "Other Problems.". However, different items loaded to these factors. While the first three factors were reliable and valid, this was not the case for the last factor. ADHD patients had higher "Breathing Problems" score than the controls, while all sleep related problems were higher in the UARS group than the other two groups. Cut-off points obtained from the ROC curves indicated that when a PSQ total score of 6 points was used as a cut-off, UARS group and the controls could be discriminated easily. In order to discriminate the ADHD and UARS groups, using the "Total Sleep Problems Score", which did not include the "Behavioral Problems" factor, resulted in greater specificty and sensitivity.
Discussion: These results indicated that the Turkish version of the PSQ was a valid and reliable measure, that the PSQ total score could discriminate patients with primary sleep disorder from healthy controls, and that the "Total Sleep Problems Score", which was obtained by omitting the Behavioral Problems factor score, could be used to discriminate primary sleep problems from secondary sleep problems associated with ADHD.
Amaç: Bu çalışmada çocuklarda uyku bozukluklarının değerlendirilmesinde kullanılan Çocuklarda Uyku Ölçeği (ÇUÖ)-uzun formunun Türkçe çevirisinin geçerlik ve güvenirliğinin belirlenmesi amaçlanmıştır. Bu ölçeğin kısaltılmış ve uzun olmak üzere 2 ayrı formu bulunmaktadır. Kısa olan form daha çok uykuya bağlı solunum problemleri ile ilişkili iken kapsamlı olan formunda, daha fazla uyku sorunu değerlendirilebilmektedir.
Yöntem: Ölçeğin Türkçe çevirisi ve geri-çeviri yapıldıktan sonra, 99 Dikkat Eksikliği Hiperaktivite Bozukluğu (DEHB) olgusu, 34 Üst Solunum yolu Direnci ve Horlaması olan (ÜSDH) olgu ve 42 sağlıklı kontrol değerlendirmeye alınmıştır. Güvenilirlik analizi için iç tutarlılık göstergesi olarak Cronbach alfa değerleri, madde-toplam puan korelasyonları ve test-tekrar test güvenirliği hesaplanmıştır. Faktörlerin belirlenmesi için ana bileşenler yöntemi ve varimax rotasyonu kullanılmıştır. Kesim noktaları, duyarlılık, özgüllük, negatif ve pozitif yordayıcı değerlerin hesaplanması için Alıcı İşlem Karakteristik Eğrileri kullanılmıştır.
Bulgular: Güvenirlik analizinde tüm ölçeğin Cronbach alfa katsayısı 0.77 olarak bulunmuştur. ÇUÖ’nin orijinal çalışmasındakine benzer bir şekilde dört faktörlü bir yapı ortaya çıkmıştır. Ancak, faktörlere farklı maddeler yüklendiği görülmüştür. Bulgular “Horlama,” “Davranış Sorunları” ve “Nefes Alma Sorunları” faktörlerinin gruplar arasında anlamlı farklar ve yeterli geçerlik ve güvenirlik gösterdiğini ancak “Diğer” faktörünün bu özellikleri sergilemediğini göstermektedir. “Nefes Alma Sorunları” DEHB grubunda kontrollerden; “Toplam Uyku Sorunları” da ÜSDH grubunda diğer iki gruptan fazla olarak saptanmıştır. Alıcı İşlem Karakteristik Eğrilerinden elde edilen kesim noktaları incelendiğinde, kesim noktası olarak ÇUÖ Toplam puanı 6 kabul edildiğinde ÜSDH ve kontrol gruplarını oldukça iyi bir şekilde ayırabildiği görülmektedir. DEHB ve ÜSDH olgularının ayrılması için “Davranış Sorunları” maddelerini içermeyen “Uyku Sorunları Toplam Puanı”nın kullanılması daha büyük bir duyarlılık ve özgüllüğe izin vermektedir.
Tartışma: ÇUÖ’nin Türkçe uyarlamasının yeterli geçerlilik ve güvenirliğe sahip olduğu, Toplam Puan’ın birincil uyku sorunu olan grubu sağlamlardan ayırt etmekte başarılı olduğu ve Davranış Sorunları puanı katılmadan bulunan Uyku Sorunları Toplam Puanı’nın birincil ve DEHB ile ilişkili ikincil uyku sorunlarının ayırt edilmesinde kullanılabileceği saptanmıştır.
Keywords: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder; Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire; reliability; snoring; upper airway resistance; validity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The validity and reliability of simplified Chinese version of the pediatric sleep questionnaire for screening children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in Beijing].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Nov 7;51(11):812-818. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2016.11.003. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27938606 Chinese.
-
Reliability and validity of the Turkish version of the pediatric sleep questionnaire: a tool for prediction of sleep related breathing disorder.Tuberk Toraks. 2011;59(3):236-41. Tuberk Toraks. 2011. PMID: 22087519
-
Translation and validation of the Arabic version of the sleep-related breathing disorder scale of the pediatric sleep questionnaire (PSQ-SRBD).Am J Otolaryngol. 2023 May-Jun;44(3):103805. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2023.103805. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Am J Otolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36871419
-
[Reliability and Validity of the Turkish Version of the Social Communication Scale.].Klinik Psikofarmakol Bulteni. 2012 Jan;22(1):43-50. doi: 10.5455/bcp.20111212091514. Klinik Psikofarmakol Bulteni. 2012. PMID: 25580078 Free PMC article. Turkish.
-
[Spanish version of the Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire (PSQ). A useful instrument in investigation of sleep disturbances in childhood. Reliability analysis].An Pediatr (Barc). 2007 Feb;66(2):121-8. doi: 10.1157/13098928. An Pediatr (Barc). 2007. PMID: 17306097 Spanish.
Cited by
-
The Effectiveness of Melatonin in Head Banging: A case report.Sleep Sci. 2019 Jan-Feb;12(1):53-56. doi: 10.5935/1984-0063.20190049. Sleep Sci. 2019. PMID: 31105896 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep Problems and Effective Factors in Preschool Children.Florence Nightingale J Nurs. 2020 Jul 3;28(2):164-173. doi: 10.5152/FNJN.2020.18063. eCollection 2020 Jun. Florence Nightingale J Nurs. 2020. PMID: 34263195 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Turkish Self-Reporting Instruments for Sleep Problems in Children, Adolescents, and Adults.Eurasian J Med. 2023 Dec;55(1):S55-S60. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2023.23309. Eurasian J Med. 2023. PMID: 39128048 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of functional independence levels on sleep and constipation in children with cerebral palsy.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2023 Nov 13;69(12):e20230765. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20230765. eCollection 2023. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2023. PMID: 37971130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meltzer LJ, Mindell JA. Nonpharmacologic treatments for pediatric sleeplessness. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2004;51:135–151. - PubMed
-
- Dahl RE, Allison GH. Sleep in children and adolescents with behavioral and emotional disorders. Sleep Med Clin. 2007;2:501–511.
-
- Van Dongen HP, Dinges DF. Investigating the interaction between the homeostatic and circadian processes of sleep-wake regulation for the prediction of waking neurobehavioural performance. J Sleep Res. 2003;12:181–187. - PubMed
-
- Chervin RD, Archbold KH, Panahi P, Pituch KJ. Sleep problems seldom addressed at two general pediatric clinics. Pediatrics. 2001;107:1375–1380. - PubMed
-
- Owens J. The practice of pediatric sleep medicine. Pediatrics. 2001;108:e51. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
