Environmental facilitators for outdoor walking and development of walking difficulty in community-dwelling older adults
- PMID: 28804315
- PMCID: PMC5549184
- DOI: 10.1007/s10433-013-0283-7
Environmental facilitators for outdoor walking and development of walking difficulty in community-dwelling older adults
Abstract
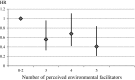
Older adults who report environmental barriers in their neighborhood have a higher risk for walking difficulty. However, environmental facilitators that protect against walking difficulty are not well known. The objective of this study was to identify the effect of environmental facilitators for outdoor walking on development of walking difficulty in community-dwelling older people. This was a prospective study with a 3.5-year follow-up time on 261 community-dwelling people aged 75-81 years, who at baseline were able to walk 0.5 km without difficulty. Environmental facilitators for outdoor walking were self-reported with standardized questionnaires, including having features in one's home which make it easy to access the outdoors, having a park or other green area within a walking distance from home, having outdoor recreational facilities within a walking distance from home, having features in the nearby environment, which are attractive for outdoor activities, and perceiving the surrounding environment or facilities nearby as motivating factors for physical activity. Self-reported difficulty in walking 0.5 km was assessed every 6 months. Of the participants, 46 % developed walking difficulty during the follow-up. Having a park or other green area within a walking distance from home was the most frequently reported facilitator. Environmental facilitators decreased the risk for development of walking difficulty, hazard ratio per item 0.86, (95 % confidence interval 0.73-1.02). The results indicate that the mobility of older community-dwelling people may be promoted with outdoor recreational facilities that are easy to access and located within a walking distance from home.
Keywords: Environmental facilitators; Mobility; Outdoor walking; Walking difficulty.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of walking modifications, perceived walking difficulty and changes in outdoor mobility among community-dwelling older people during COVID-19 restrictions.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021 Oct;33(10):2909-2916. doi: 10.1007/s40520-021-01956-2. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 34417731 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived environmental barriers to outdoor mobility and feelings of loneliness among community-dwelling older people.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014 Dec;69(12):1562-8. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glu069. Epub 2014 May 26. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24864307
-
Short-term effects of a park-based group mobility program on increasing outdoor walking in older adults with difficulty walking outdoors: the Getting Older Adults Outdoors (GO-OUT) randomized controlled trial.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Sep 6;24(1):740. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05331-4. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 39243012 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Factors Associated with Outdoor Winter Walking in Older Adults: A Scoping Review.Can J Aging. 2023 Jun;42(2):316-327. doi: 10.1017/S0714980822000460. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Can J Aging. 2023. PMID: 36458993
-
Outdoor Community Ambulation Interventions to Improve Physical and Mental Health in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Aging Phys Act. 2022 Apr 13;30(6):1061-1074. doi: 10.1123/japa.2021-0151. Print 2022 Dec 1. J Aging Phys Act. 2022. PMID: 35418512
Cited by
-
Associations between walking limitations and reported activity destinations among older adults.Eur J Ageing. 2024 May 22;21(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s10433-024-00813-1. Eur J Ageing. 2024. PMID: 38775867 Free PMC article.
-
A park-based group mobility program for older adults with difficulty walking outdoors: a qualitative process evaluation of the Getting Older Adults Outdoors (GO-OUT) randomized controlled trial.BMC Geriatr. 2025 Jan 8;25(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05611-z. BMC Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 39780066 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Projections of dependency and associated social care expenditure for the older population in England to 2038: effect of varying disability progression.Age Ageing. 2022 Jul 1;51(7):afac158. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afac158. Age Ageing. 2022. PMID: 35871421 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental mobility barriers and walking for errands among older people who live alone vs. with others.BMC Public Health. 2013 Nov 8;13:1054. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-1054. BMC Public Health. 2013. PMID: 24207063 Free PMC article.
-
Older Adults' Physical Activity and the Relevance of Distances to Neighborhood Destinations and Barriers to Outdoor Mobility.Front Public Health. 2020 Aug 7;8:335. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00335. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32850580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caspersen CJ. Physical activity epidemiology: concepts, methods, and applications to exercise science. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1989;17:423–473. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources