Risk of Selected Cardiovascular Toxicities in Patients With Cancer Treated With MEK Inhibitors: A Comparative Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 28804776
- PMCID: PMC5539872
- DOI: 10.1200/JGO.2015.000802
Risk of Selected Cardiovascular Toxicities in Patients With Cancer Treated With MEK Inhibitors: A Comparative Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: We conducted a literature-based meta-analysis of the risk of cardiovascular toxicities associated with MEK inhibitors.
Methods: Eligible trials included randomized phase II and III trials of patients with cancer who were given a mitogen activated protein (MAP)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase (MEK) inhibitor (trametinib, selumetinib, or cobimetinib) and that described events of hypertension and decreased ejection fraction.
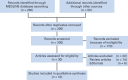
Results: Our search strategy yielded 300 potentially relevant citations from PubMed/MEDLINE, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. After ineligible studies were excluded, a total of 10 clinical trials were considered eligible for the meta-analysis. The relative risk for all grades of hypertension was 1.54 (95% CI, 1.02 to 2.32; P = .05), 1.85 (95% CI, 1.01 to 3.40; P = .05) for high-grade hypertension, and 4.92 (95% CI, 2.93 to 8.25; P < .001) for decreased ejection fraction. Subgroup analysis revealed no difference between trametinib and selumetinib for risk of hypertension.
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis demonstrated that MEK inhibitor-based treatment is associated with an increased risk of all-grade and high-grade hypertension and asymptomatic decrease in ejection fraction. Clinicians should be aware of this risk and perform regular assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and contributions are found at the end of this article.The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or jco.ascopubs.org/site/ifc. Omar Abdel-RahmanNo relationship to discloseHesham ElHalawaniNo relationship to discloseHoda AhmedNo relationship to disclose
Figures





References
-
- Marzuka A Huang L Theodosakis N, etal: Melanoma treatments: Advances and mechanisms J Cell Physiol 230:2626–2633,2015 - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal C: Targeted therapy for lung cancer: Present and future Ann Palliat Med 3:229–235,2014 - PubMed
-
- Dossett LA, Kudchadkar RR, Zager JS: BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma Expert Opin Drug Saf 14:559–570,2015 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

