Safety and Efficacy of Intravenous Golimumab in Patients With Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Results Through Week Twenty-Four of the GO-VIBRANT Study
- PMID: 28805045
- PMCID: PMC5765449
- DOI: 10.1002/art.40226
Safety and Efficacy of Intravenous Golimumab in Patients With Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Results Through Week Twenty-Four of the GO-VIBRANT Study
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of intravenous (IV) golimumab treatment in psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
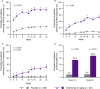
Methods: In this phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, patients were randomly assigned to receive IV placebo (n = 239) or golimumab at 2 mg/kg (n = 241) at weeks 0, 4, 12, and 20. The primary end point was the proportion of patients meeting the American College of Rheumatology 20% improvement criteria (achieving an ACR20 response) at week 14. Controlled secondary end points included change from baseline in Health Assessment Questionnaire disability index (HAQ DI) score at week 14, proportions of patients with ACR50 and ACR70 responses and ≥75% improvement on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (a PASI75 response) at week 14, and change from baseline at week 24 in the total modified Sharp/van der Heijde score (SHS) with modifications for patients with PsA.
Results: At week 14, an ACR20 response was achieved by 75.1% of patients in the golimumab group compared with 21.8% of patients in the placebo group (P < 0.001). Greater proportions of golimumab-treated patients had an ACR50 response (43.6% versus 6.3%), an ACR70 response (24.5% versus 2.1%), and a PASI75 response (59.2% versus 13.6%) at week 14 (P < 0.001 for all). Patients in the golimumab group had greater mean changes at week 14 in HAQ DI score (-0.60 versus -0.12; P < 0.001). At week 24, the mean change in total PsA-modified SHS was -0.4 in the golimumab group and 2.0 in the placebo group (P < 0.001). Through week 24, 40.6% of patients in the placebo group and 46.3% of patients in the golimumab group had ≥1 adverse event (AE); infections were the most common type.
Conclusion: Patients receiving IV golimumab at 2 mg/kg had significantly greater improvements in the signs and symptoms of PsA and less radiographic progression through week 24. AEs were consistent with those seen with other anti-tumor necrosis factor agents.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02181673.
© 2017 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Figures


References
-
- Raychaudhuri SP, Wilken R, Sukhov AC, Raychaudhuri SK, Maverakis E. Management of psoriatic arthritis: early diagnosis, monitoring of disease severity and cutting edge therapies. J Autoimmun 2017;76:21–37. - PubMed
-
- Coates LC, Kavanaugh A, Mease PJ, Soriano ER, Acosta‐Felquer ML, Armstrong AW, et al. Group for research and assessment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis 2015 treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:1060–71. - PubMed
-
- Gossec L, Smolen JS, Ramiro S, de Wit M, Cutolo M, Dougados M, et al. European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies: 2015 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:499–510. - PubMed
-
- Kavanaugh A, McInnes I, Mease P, Krueger GG, Gladman D, Gomez‐Reino J, et al. Golimumab, a new human tumor necrosis factor α antibody, administered every four weeks as a subcutaneous injection in psoriatic arthritis: twenty‐four–week efficacy and safety results of a randomized, placebo‐controlled study. Arthritis Rheum 2009;60:976–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

