Bisphosphoglycerate mutase controls serine pathway flux via 3-phosphoglycerate
- PMID: 28805803
- PMCID: PMC5605442
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.2453
Bisphosphoglycerate mutase controls serine pathway flux via 3-phosphoglycerate
Abstract
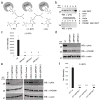
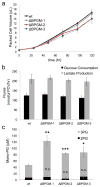
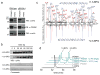
Lower glycolysis involves a series of reversible reactions, which interconvert intermediates that also feed anabolic pathways. 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PG) is an abundant lower glycolytic intermediate that feeds serine biosynthesis via the enzyme phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase, which is genomically amplified in several cancers. Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 (PGAM1) catalyzes the isomerization of 3-PG into the downstream glycolytic intermediate 2-phosphoglycerate (2-PG). PGAM1 needs to be histidine phosphorylated to become catalytically active. We show that the primary PGAM1 histidine phosphate donor is 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG), which is made from the glycolytic intermediate 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG) by bisphosphoglycerate mutase (BPGM). When BPGM is knocked out, 1,3-BPG can directly phosphorylate PGAM1. In this case, PGAM1 phosphorylation and activity are decreased, but nevertheless sufficient to maintain normal glycolytic flux and cellular growth rate. 3-PG, however, accumulates, leading to increased serine synthesis. Thus, one biological function of BPGM is controlling glycolytic intermediate levels and thereby serine biosynthetic flux.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Labuschagne CF, van den Broek NJ, Mackay GM, Vousden KH, Maddocks OD. Serine, but not glycine, supports one-carbon metabolism and proliferation of cancer cells. Cell Rep. 2014;7:1248–58. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

