Suppression of acute and anticipatory nausea by peripherally restricted fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor in animal models: role of PPARα and CB1 receptors
- PMID: 28805944
- PMCID: PMC5647182
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13980
Suppression of acute and anticipatory nausea by peripherally restricted fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor in animal models: role of PPARα and CB1 receptors
Abstract
Background and purpose: Effective treatments of nausea are limited. In this study we evaluated the ability of the peripherally restricted fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitor, URB937, to suppress acute and anticipatory nausea in rats and examined the pharmacological mechanism of this effect.
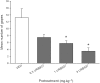
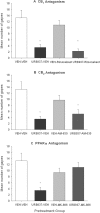
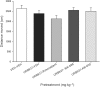
Experimental approach: We investigated the potential of URB937 (administered i.p.) to reduce the establishment of lithium chloride-induced conditioned gaping (model of acute nausea) and to reduce the expression of contextually-elicited conditioned gaping (model of anticipatory nausea) in rats. The role of CB1 receptors, CB2 receptors and PPARα in the anti-nausea effect of URB937 was examined. The potential of URB937 to suppress FAAH activity in tissue collected from the area postrema (AP), prefrontal cortex (PFC), liver and duodenum and to elevate levels of FAAH substrates - anandamide (AEA), N-oleoylethanolamide (OEO) and N-palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) - in the AP was also evaluated.
Key results: URB937 reduced acute nausea by a PPARα-dependent mechanism and reduced anticipatory nausea by a CB1 receptor-dependent mechanism. The PPARα agonist, GW7647, similarly attenuated acute nausea. URB937 reduced FAAH activity in the liver and the duodenum but not in the PFC. In addition, URB937 reduced FAAH activity and elevated levels of fatty-acid ethanolamides in the AP, a brain region that is not protected by the blood-brain barrier.
Conclusions and implications: The anti-nausea action of URB937 may occur in the AP and may involve PPARα to suppress acute nausea and CB1 receptors to suppress anticipatory nausea.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

