In vitro pharmacological characterization of a novel unbiased NOP receptor-selective nonpeptide agonist AT-403
- PMID: 28805972
- PMCID: PMC5684865
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.333
In vitro pharmacological characterization of a novel unbiased NOP receptor-selective nonpeptide agonist AT-403
Abstract
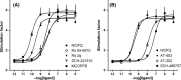
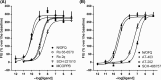
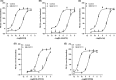
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) regulates several biological functions via selective activation of the N/OFQ receptor (NOP), a member of the opioid receptor family. We recently identified a new high affinity and highly selective NOP agonist AT-403. In this study, we characterized the functional profile of AT-403 and compared it to other known nonpeptide NOP agonists Ro 65-6570, Ro 2q, SCH-221510, MCOPPB, AT-202 and SCH-486757, using the following assays: GTPγ[35 S] stimulated binding, calcium mobilization assay in cells-expressing human NOP or classical opioid receptors and chimeric G proteins, bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) based assay for studying NOP receptor interaction with G protein and arrestin, and the electrically stimulated mouse vas deferens bioassay. All compounds behaved as NOP full agonists consistently showing the following rank order of potency MCOPPB > AT-403 > Ro 65-6570 = Ro 2q > SCH-221510 > AT-202 > SCH-486757. AT-403 and MCOPPB displayed the highest NOP selectivity both at human and murine receptors. Interestingly, while all the other nonpeptide NOP agonists displayed bias toward G protein-mediated signaling in the BRET assay, AT-403, similar to the natural ligand N/OFQ, behaved as an unbiased agonist, activating G-protein-mediated function as well as arrestin recruitment. AT-403 may be a useful nonpeptide tool compound to study the pharmacology of NOP activation in disease states.
Keywords: BRET arrestin assay; GPCR signaling bias; NOP receptor; functional selectivity; ligand bias; nonpeptide NOP agonists.
© 2017 The Authors. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd, British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures







References
-
- Bertorelli R, Bastia E, Citterio F, Corradini L, Forlani A, Ongini E (2002). Lack of the nociceptin receptor does not affect acute or chronic nociception in mice. Peptides 23: 1589–1596. - PubMed
-
- Berzetei‐Gurske IP, Schwartz RW, Toll L (1996). Determination of activity for nociceptin in the mouse vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol 302: R1–2. - PubMed
-
- Calo G, Rizzi A, Bogoni G, Neugebauer V, Salvadori S, Guerrini R, et al. (1996). The mouse vas deferens: a pharmacological preparation sensitive to nociceptin. Eur J Pharmacol 311: R3–5. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

