Speech Perception in Noise and Listening Effort of Older Adults With Nonlinear Frequency Compression Hearing Aids
- PMID: 28806193
- PMCID: PMC5809244
- DOI: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000481
Speech Perception in Noise and Listening Effort of Older Adults With Nonlinear Frequency Compression Hearing Aids
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this laboratory-based study was to compare the efficacy of two hearing aid fittings with and without nonlinear frequency compression, implemented within commercially available hearing aids. Previous research regarding the utility of nonlinear frequency compression has revealed conflicting results for speech recognition, marked by high individual variability. Individual differences in auditory function and cognitive abilities, specifically hearing loss slope and working memory, may contribute to aided performance. The first aim of the study was to determine the effect of nonlinear frequency compression on aided speech recognition in noise and listening effort using a dual-task test paradigm. The hypothesis, based on the Ease of Language Understanding model, was that nonlinear frequency compression would improve speech recognition in noise and decrease listening effort. The second aim of the study was to determine if listener variables of hearing loss slope, working memory capacity, and age would predict performance with nonlinear frequency compression.
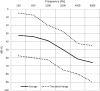
Design: A total of 17 adults (age, 57-85 years) with symmetrical sensorineural hearing loss were tested in the sound field using hearing aids fit to target (NAL-NL2). Participants were recruited with a range of hearing loss severities and slopes. A within-subjects, single-blinded design was used to compare performance with and without nonlinear frequency compression. Speech recognition in noise and listening effort were measured by adapting the Revised Speech in Noise Test into a dual-task paradigm. Participants were required trial-by-trial to repeat the last word of each sentence presented in speech babble and then recall the sentence-ending words after every block of six sentences. Half of the sentences were rich in context for the recognition of the final word of each sentence, and half were neutral in context. Extrinsic factors of sentence context and nonlinear frequency compression were manipulated, and intrinsic factors of hearing loss slope, working memory capacity, and age were measured to determine which participant factors were associated with benefit from nonlinear frequency compression.
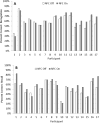
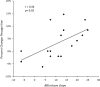
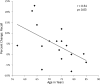
Results: On average, speech recognition in noise performance significantly improved with the use of nonlinear frequency compression. Individuals with steeply sloping hearing loss received more recognition benefit. Recall performance also significantly improved at the group level, with nonlinear frequency compression revealing reduced listening effort. The older participants within the study cohort received less recall benefit than the younger participants. The benefits of nonlinear frequency compression for speech recognition and listening effort did not correlate with each other, suggesting separable sources of benefit for these outcome measures.
Conclusions: Improvements of speech recognition in noise and reduced listening effort indicate that adult hearing aid users can receive benefit from nonlinear frequency compression in a noisy environment, with the amount of benefit varying across individuals and across outcome measures. Evidence supports individualized selection of nonlinear frequency compression, with results suggesting benefits in speech recognition for individuals with steeply sloping hearing losses and in listening effort for younger individuals. Future research is indicated with a larger data set on the dual-task paradigm as a potential cognitive outcome measure.
Figures

Similar articles
-
How hearing aids, background noise, and visual cues influence objective listening effort.Ear Hear. 2013 Sep;34(5):e52-64. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0b013e31827f0431. Ear Hear. 2013. PMID: 23416751
-
The effects of hearing aid use on listening effort and mental fatigue associated with sustained speech processing demands.Ear Hear. 2013 Sep;34(5):523-34. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0b013e31828003d8. Ear Hear. 2013. PMID: 23426091
-
Do hearing loss and cognitive function modulate benefit from different binaural noise-reduction settings?Ear Hear. 2014 May-Jun;35(3):e52-62. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000003. Ear Hear. 2014. PMID: 24351610
-
A critical review of hearing-aid single-microphone noise-reduction studies in adults and children.Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2018 Aug;13(6):600-608. doi: 10.1080/17483107.2017.1392619. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2018. PMID: 29072542 Review.
-
The Effect of Cognition on the Aided Benefit in Terms of Speech Understanding and Listening Effort Obtained With Digital Hearing Aids: A Systematic Review.Am J Audiol. 2021 Mar 10;30(1):190-210. doi: 10.1044/2020_AJA-20-00019. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Am J Audiol. 2021. PMID: 33524267
Cited by
-
Hearing and speech processing in midlife.Hear Res. 2021 Mar 15;402:108097. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2020.108097. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Hear Res. 2021. PMID: 33706999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of auditory processing and cognitive change during normal ageing, and the implications for setting hearing aids for older adults.Front Neurol. 2023 Jun 20;14:1122420. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1122420. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37409017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Audibility and Spectral-Ripple Discrimination Thresholds as Predictors of Word Recognition with Nonlinear Frequency Compression.J Am Acad Audiol. 2021 Oct;32(9):596-605. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1732333. Epub 2022 Feb 17. J Am Acad Audiol. 2021. PMID: 35176803 Free PMC article.
-
Lipreading: A Review of Its Continuing Importance for Speech Recognition With an Acquired Hearing Loss and Possibilities for Effective Training.Am J Audiol. 2022 Jun 2;31(2):453-469. doi: 10.1044/2021_AJA-21-00112. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Am J Audiol. 2022. PMID: 35316072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding Variability in Individual Response to Hearing Aid Signal Processing in Wearable Hearing Aids.Ear Hear. 2019 Nov/Dec;40(6):1280-1292. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000717. Ear Hear. 2019. PMID: 30998547 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Akeroyd MA. Are individual differences in speech reception related to individual differences in cognitive ability? A survey of twenty experimental studies with normal and hearing-impaired adults. International Journal of Audiology. 2008;47(S2):S53–S71. - PubMed
-
- Alexander JM. Individual variability in recognition of frequency-lowered speech. Seminars in Hearing. 2013;34(2):86–109.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

