A Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) layer implemented over i2b2
- PMID: 28806953
- PMCID: PMC5557515
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-017-0513-6
A Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) layer implemented over i2b2
Abstract
Background: Standards and technical specifications have been developed to define how the information contained in Electronic Health Records (EHRs) should be structured, semantically described, and communicated. Current trends rely on differentiating the representation of data instances from the definition of clinical information models. The dual model approach, which combines a reference model (RM) and a clinical information model (CIM), sets in practice this software design pattern. The most recent initiative, proposed by HL7, is called Fast Health Interoperability Resources (FHIR). The aim of our study was to investigate the feasibility of applying the FHIR standard to modeling and exposing EHR data of the Georges Pompidou European Hospital (HEGP) integrating biology and the bedside (i2b2) clinical data warehouse (CDW).
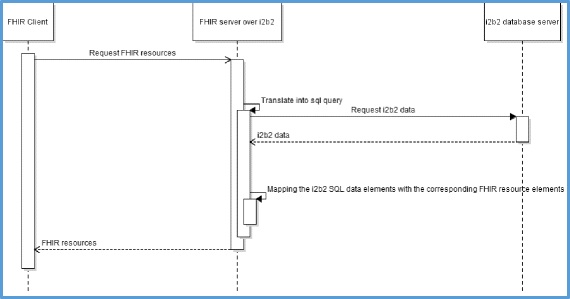
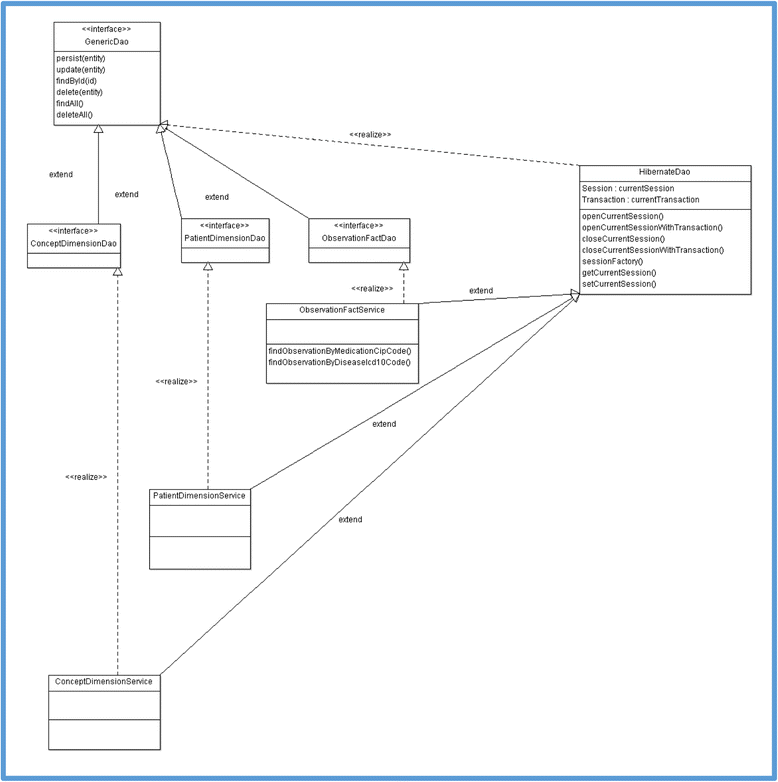
Results: We implemented a FHIR server over i2b2 to expose EHR data in relation with five FHIR resources: DiagnosisReport, MedicationOrder, Patient, Encounter, and Medication. The architecture of the server combines a Data Access Object design pattern and FHIR resource providers, implemented using the Java HAPI FHIR API. Two types of queries were tested: query type #1 requests the server to display DiagnosticReport resources, for which the diagnosis code is equal to a given ICD-10 code. A total of 80 DiagnosticReport resources, corresponding to 36 patients, were displayed. Query type #2, requests the server to display MedicationOrder, for which the FHIR Medication identification code is equal to a given code expressed in a French coding system. A total of 503 MedicationOrder resources, corresponding to 290 patients, were displayed. Results were validated by manually comparing the results of each request to the results displayed by an ad-hoc SQL query.
Conclusion: We showed the feasibility of implementing a Java layer over the i2b2 database model to expose data of the CDW as a set of FHIR resources. An important part of this work was the structural and semantic mapping between the i2b2 model and the FHIR RM. To accomplish this, developers must manually browse the specifications of the FHIR standard. Our source code is freely available and can be adapted for use in other i2b2 sites.
Keywords: Clinical data warehouse; Database management systems; FHIR; Semantic interoperability; i2b2.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
In this article we accessed clinical data to perform tests on the fhir server. Clinical data were accessed from the clinical data warehouse repository of the Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou (Georges Pompidou European Hospital).
This work is part of the IM-AGE project which received ethics approval and permission to access patient clinical data from a local French IRB (Comité de Protection des Personnes, Ile de France II):
IRB registration number: 00001072.
Date: 12/07/2015
IRB address: 149, rue Sèvres 75,743 Paris cedex 15. Carré Necker – Porte N2. Phone: 0142192688, Fax: 0144494506.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
A.B. and E.Z. declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures






References
-
- Prokosch HU, Ganslandt T. Perspectives for medical informatics. Reusing the electronic medical record for clinical research. Methods Inf Med. 2009;48(1):38–44. - PubMed
-
- De Moor G. EHR-certification, semantic interoperability and the link to clinical research [Internet]. eHealth-WoHIT conference; 2010 [cited 2017 Mar 2]. Available from: https://pt.slideshare.net/sanidadyconsumo/ehr-certification-semantic-int....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

