The impact of active stakeholder involvement on recruitment, retention and engagement of schools, children and their families in the cluster randomised controlled trial of the Healthy Lifestyles Programme (HeLP): a school-based intervention to prevent obesity
- PMID: 28807006
- PMCID: PMC5557526
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-2122-1
The impact of active stakeholder involvement on recruitment, retention and engagement of schools, children and their families in the cluster randomised controlled trial of the Healthy Lifestyles Programme (HeLP): a school-based intervention to prevent obesity
Abstract
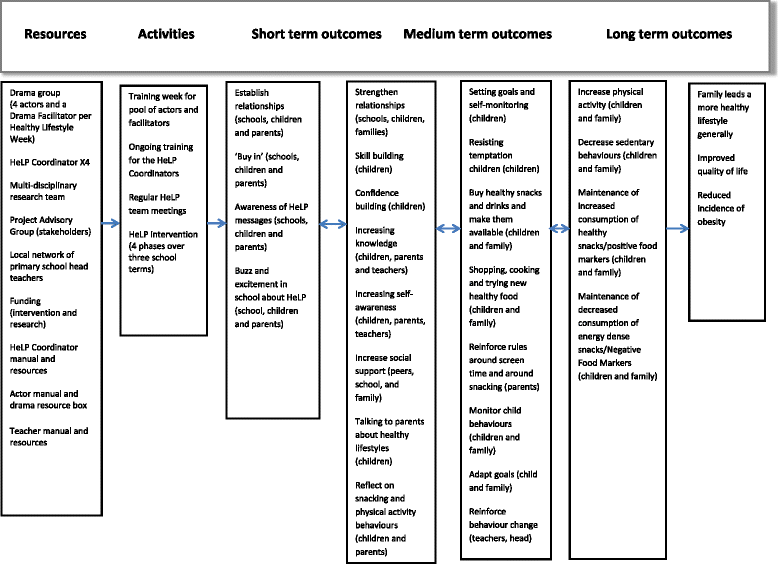
Background: Recruitment and retention of participants is crucial for statistical power and internal and external validity and participant engagement is essential for behaviour change. However, many school-based interventions focus on programme content rather than the building of supportive relationships with all participants and tend to employ specific standalone strategies, such as incentives, to improve retention. We believe that actively involving stakeholders in both intervention and trial design improves recruitment and retention and increases the chances of creating an effective intervention.
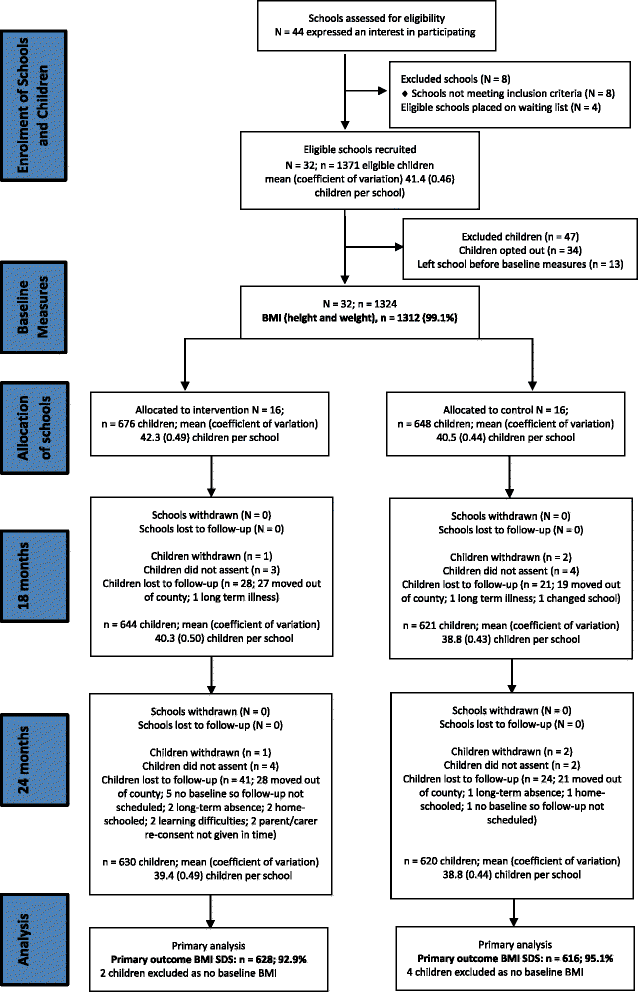
Methods: The Healthy Lifestyles Programme, HeLP (an obesity prevention programme for children 9-10 years old) was developed using intervention mapping and involved extensive stakeholder involvement in both the design of the trial and the intervention to ensure that: (i) delivery methods were suitably engaging, (ii) deliverers had the necessary skills and qualities to build relationships and (iii) the intervention dovetailed with the National Curriculum. HeLP was a year-long intervention consisting of 4 multi-component phases using a range of delivery methods. We recruited 1324 children from 32 schools from the South West of England to a cluster-randomised controlled trial to determine the effectiveness of HeLP in preventing obesity. The primary outcome was change in body mass index standard deviation score (BMI SDS) at 24 months post randomisation. Secondary outcomes included additional anthropometric and behavioural (physical activity and diet) measures at 18 and 24 months.
Results: Anthropometric and behavioural measures were taken in 99%, 96% and 94% of children at baseline, 18 and 24 months, respectively, with no differential follow up between the control and intervention groups at each time point. All children participated in the programme and 92% of children and 77% of parents across the socio-economic spectrum were considered to have actively engaged with HeLP.
Conclusions: We attribute our excellent retention and engagement results to the high level of stakeholder involvement in both trial and intervention design, the building of relationships using appropriate personnel and creative delivery methods that are accessible to children and their families across the social spectrum.
Trial registration: International Standard Randomised Controlled Trials Register, ISRCTN15811706 . Registered on 1 May 2012.
Keywords: Child; Cluster RCT; Complex intervention; Engagement; Obesity prevention; Recruitment; Retention; School; Stakeholder involvement.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval for the trial was obtained from the Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry in March 2012 (reference number 12/03/140). Parental consent for participation in the study and permission to publish anonymised data was obtained from all participating children using an opt-out approach.
Consent for publication
Not applicable as the manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Polit DF, Beck CT. Nursing research: Principles and methods. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

