A protein complex regulates RNA processing of intronic heterochromatin-containing genes in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 28808009
- PMCID: PMC5584460
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1710683114
A protein complex regulates RNA processing of intronic heterochromatin-containing genes in Arabidopsis
Abstract
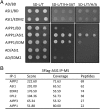
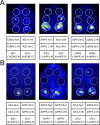
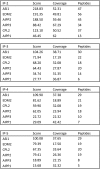
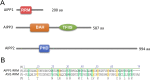
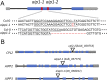
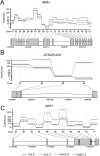
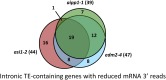
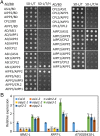
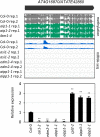
In several eukaryotic organisms, heterochromatin (HC) in the introns of genes can regulate RNA processing, including polyadenylation, but the mechanism underlying this regulation is poorly understood. By promoting distal polyadenylation, the bromo-adjacent homology (BAH) domain-containing and RNA recognition motif-containing protein ASI1 and the H3K9me2-binding protein EDM2 are required for the expression of functional full-length transcripts of intronic HC-containing genes in Arabidopsis Here we report that ASI1 and EDM2 form a protein complex in vivo via a bridge protein, ASI1-Immunoprecipitated Protein 1 (AIPP1), which is another RNA recognition motif-containing protein. The complex also may contain the Pol II CTD phosphatase CPL2, the plant homeodomain-containing protein AIPP2, and another BAH domain protein, AIPP3. As is the case with dysfunction of ASI1 and EDM2, dysfunction of AIPP1 impedes the use of distal polyadenylation sites at tested intronic HC-containing genes, such as the histone demethylase gene IBM1, resulting in a lack of functional full-length transcripts. A mutation in AIPP1 causes silencing of the 35S-SUC2 transgene and genome-wide CHG hypermethylation at gene body regions, consistent with the lack of full-length functional IBM1 transcripts in the mutant. Interestingly, compared with asi1, edm2, and aipp1 mutations, mutations in CPL2, AIPP2, and AIPP3 cause the opposite effects on the expression of intronic HC-containing genes and other genes, suggesting that CPL2, AIPP2, and AIPP3 may form a distinct subcomplex. These results advance our understanding of the interplay between heterochromatic epigenetic modifications and RNA processing in higher eukaryotes.
Keywords: DNA methylation; RNA processing; heterochromatin; polyadenylation; transposable element.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA-binding protein regulates plant DNA methylation by controlling mRNA processing at the intronic heterochromatin-containing gene IBM1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Sep 17;110(38):15467-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315399110. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24003136 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism for full-length RNA processing of Arabidopsis genes containing intragenic heterochromatin.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2301. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3301. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23934508
-
Arabidopsis EDM2 promotes IBM1 distal polyadenylation and regulates genome DNA methylation patterns.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 7;111(1):527-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320106110. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24248388 Free PMC article.
-
Heterochromatin proteins and the control of heterochromatic gene silencing in Arabidopsis.J Plant Physiol. 2006 Feb;163(3):358-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2005.10.015. Epub 2005 Dec 27. J Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16384625 Review.
-
Transcription of the 5S rRNA heterochromatic genes is epigenetically controlled in Arabidopsis thaliana and Xenopus laevis.Heredity (Edinb). 2007 Jul;99(1):5-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800964. Epub 2007 May 9. Heredity (Edinb). 2007. PMID: 17487217 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA methylation-free Arabidopsis reveals crucial roles of DNA methylation in regulating gene expression and development.Nat Commun. 2022 Mar 14;13(1):1335. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28940-2. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35288562 Free PMC article.
-
HDA6-dependent histone deacetylation regulates mRNA polyadenylation in Arabidopsis.Genome Res. 2020 Oct;30(10):1407-1417. doi: 10.1101/gr.255232.119. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Genome Res. 2020. PMID: 32759225 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Methylation Patterns in Apomictic vs. Sexual Genotypes of the Diplosporous Grass Eragrostis curvula.Plants (Basel). 2021 May 10;10(5):946. doi: 10.3390/plants10050946. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34068493 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic Actions of FPA and IBM2 Regulate Transcript Processing from Genes Containing Heterochromatin.Plant Physiol. 2019 May;180(1):392-403. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01106. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Plant Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30814131 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis PHD-finger protein EDM2 has multiple roles in balancing NLR immune receptor gene expression.PLoS Genet. 2020 Sep 14;16(9):e1008993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008993. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32925902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rebollo R, Romanish MT, Mager DL. Transposable elements: An abundant and natural source of regulatory sequences for host genes. Annu Rev Genet. 2012;46:21–42. - PubMed
-
- Bennetzen JL, Wang H. The contributions of transposable elements to the structure, function, and evolution of plant genomes. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2014;65:505–530. - PubMed
-
- Zemach A, McDaniel IE, Silva P, Zilberman D. Genome-wide evolutionary analysis of eukaryotic DNA methylation. Science. 2010;328:916–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

