Mutations in eIF5B Confer Thermosensitive and Pleiotropic Phenotypes via Translation Defects in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 28808135
- PMCID: PMC5590492
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.16.00808
Mutations in eIF5B Confer Thermosensitive and Pleiotropic Phenotypes via Translation Defects in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
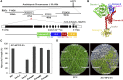
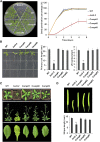
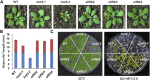
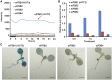
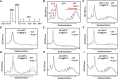
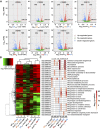
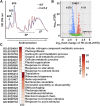
The conserved eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B, eIF5B, is a GTPase that acts late in translation initiation. We found that an Arabidopsis thaliana mutant sensitive to hot temperatures 3 (hot3-1), which behaves as the wild type in the absence of stress but is unable to acclimate to high temperature, carries a missense mutation in the eIF5B1 gene (At1g76810), producing a temperature sensitive protein. A more severe, T-DNA insertion allele (hot3-2) causes pleiotropic developmental phenotypes. Surprisingly, Arabidopsis has three other eIF5B genes that do not substitute for eIF5B1; two of these appear to be in the process of pseudogenization. Polysome profiling and RNA-seq analysis of hot3-1 plants show delayed recovery of polysomes after heat stress and reduced translational efficiency (TE) of a subset of stress protective proteins, demonstrating the critical role of translational control early in heat acclimation. Plants carrying the severe hot3-2 allele show decreased TE of auxin-regulated, ribosome-related, and electron transport genes, even under optimal growth conditions. The hot3-2 data suggest that disrupting specific eIF5B interactions on the ribosome can, directly or indirectly, differentially affect translation. Thus, modulating eIF5B interactions could be another mechanism of gene-specific translational control.
© 2017 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Some Like It HOT: Protein Translation and Heat Stress in Plants.Plant Cell. 2017 Sep;29(9):2075. doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00699. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Plant Cell. 2017. PMID: 28874510 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
HOT3/eIF5B1 confers Kozak motif-dependent translational control of photosynthesis-associated nuclear genes for chloroplast biogenesis.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 14;15(1):9878. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54194-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39543117 Free PMC article.
-
Translational regulation via 5' mRNA leader sequences revealed by mutational analysis of the Arabidopsis translation initiation factor subunit eIF3h.Plant Cell. 2004 Dec;16(12):3341-56. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.026880. Epub 2004 Nov 17. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15548739 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis HOT3/eIF5B1 constrains rRNA RNAi by facilitating 18S rRNA maturation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Apr 11;120(15):e2301081120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2301081120. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37011204 Free PMC article.
-
The heat responsive wheat TaRAD23 rescues developmental and thermotolerant defects of the rad23b mutant in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Sci. 2018 Sep;274:23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.04.028. Epub 2018 May 3. Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30080608 Review.
-
Established and Emerging Regulatory Roles of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 5B (eIF5B).Front Genet. 2021 Aug 27;12:737433. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.737433. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34512736 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reprogramming of Root Cells during Nitrogen-Fixing Symbiosis Involves Dynamic Polysome Association of Coding and Noncoding RNAs.Plant Cell. 2020 Feb;32(2):352-373. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00647. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 31748328 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of mRNA fate during light stress and recovery: from transcription to stability and translation.Plant J. 2024 Feb;117(3):818-839. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16531. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 37947266 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Variation in RNA m6A Methylation and Its Relationship with Translational Status.Plant Physiol. 2020 Jan;182(1):332-344. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00987. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Plant Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31591151 Free PMC article.
-
Polysomes, Stress Granules, and Processing Bodies: A Dynamic Triumvirate Controlling Cytoplasmic mRNA Fate and Function.Plant Physiol. 2018 Jan;176(1):254-269. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01468. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29158329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Musashi Splice Variant and Its Interaction Partners Influence Temperature Acclimation in Chlamydomonas.Plant Physiol. 2018 Dec;178(4):1489-1506. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00972. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30301774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acker M.G., Shin B.S., Dever T.E., Lorsch J.R. (2006). Interaction between eukaryotic initiation factors 1A and 5B is required for efficient ribosomal subunit joining. J. Biol. Chem. 281: 8469–8475. - PubMed
-
- Carrera P., Johnstone O., Nakamura A., Casanova J., Jäckle H., Lasko P. (2000). VASA mediates translation through interaction with a Drosophila yIF2 homolog. Mol. Cell 5: 181–187. - PubMed
-
- Choi S.K., Lee J.H., Zoll W.L., Merrick W.C., Dever T.E. (1998). Promotion of met-tRNAiMet binding to ribosomes by yIF2, a bacterial IF2 homolog in yeast. Science 280: 1757–1760. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

