Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α Promotes Pulmonary Inflammation and Systemic Disease during Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection
- PMID: 28808157
- PMCID: PMC5649009
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00280-17
Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α Promotes Pulmonary Inflammation and Systemic Disease during Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection
Abstract
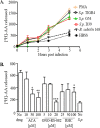
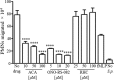
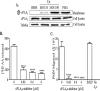
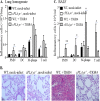
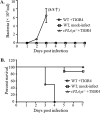
Pulmonary infection by Streptococcus pneumoniae is characterized by a robust alveolar infiltration of neutrophils (polymorphonuclear cells [PMNs]) that can promote systemic spread of the infection if not resolved. We previously showed that 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX), which is required to generate the PMN chemoattractant hepoxilin A3 (HXA3) from arachidonic acid (AA), promotes acute pulmonary inflammation and systemic infection after lung challenge with S. pneumoniae As phospholipase A2 (PLA2) promotes the release of AA, we investigated the role of PLA2 in local and systemic disease during S. pneumoniae infection. The group IVA cytosolic isoform of PLA2 (cPLA2α) was activated upon S. pneumoniae infection of cultured lung epithelial cells and was critical for AA release from membrane phospholipids. Pharmacological inhibition of this enzyme blocked S. pneumoniae-induced PMN transepithelial migration in vitro Genetic ablation of the cPLA2 isoform cPLA2α dramatically reduced lung inflammation in mice upon high-dose pulmonary challenge with S. pneumoniae The cPLA2α-deficient mice also suffered no bacteremia and survived a pulmonary challenge that was lethal to wild-type mice. Our data suggest that cPLA2α plays a crucial role in eliciting pulmonary inflammation during pneumococcal infection and is required for lethal systemic infection following S. pneumoniae lung challenge.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; inflammation; neutrophils; phospholipase.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- McCullers JA, Tuomanen EI. 2001. Molecular pathogenesis of pneumococcal pneumonia. Front Biosci 6:D877–D889. - PubMed
-
- Lynch JP III, Zhanel GG. 2010. Streptococcus pneumoniae: epidemiology and risk factors, evolution of antimicrobial resistance, and impact of vaccines. Curr Opin Pulm Med 16:217–225. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien KL, Wolfson LJ, Watt JP, Henkle E, Deloria-Knoll M, McCall N, Lee E, Mulholland K, Levine OS, Cherian T. 2009. Hib and Pneumococcal Global Burden of Disease Study Team: burden of disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in children younger than 5 years: global estimates. Lancet 374:893–902. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61204-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Doerschuk CM, Markos J, Coxson HO, English D, Hogg JC. 1994. Quantitation of neutrophil migration in acute bacterial pneumonia in rabbits. J Appl Physiol 77:2593–2599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

