Metabolomic profiles of plasma, exhaled breath condensate, and saliva are correlated with potential for air toxics detection
- PMID: 28808178
- PMCID: PMC5803078
- DOI: 10.1088/1752-7163/aa863c
Metabolomic profiles of plasma, exhaled breath condensate, and saliva are correlated with potential for air toxics detection
Abstract
Introduction: Advances in the development of high-resolution metabolomics (HRM) have provided new opportunities for their use in characterizing exposures to environmental air pollutants and air pollution-related disease etiologies. Exposure assessment studies have considered blood, breath, and saliva as biological matrices suitable for measuring responses to air pollution exposures. The current study examines comparability among these three matrices using HRM and explores their potential for measuring mobile-source air toxics.
Methods: Four participants provided saliva, exhaled breath concentrate (EBC), and plasma before and after a 2 h road traffic exposure. Samples were analyzed on a Thermo Scientific QExactive MS system in positive electrospray ionization mode and resolution of 70 000 full-width at half-maximum with C18 chromatography. Data were processed using an apLCMS and xMSanalyzer on the R statistical platform.
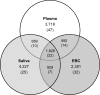
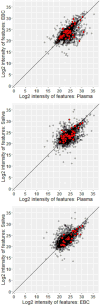
Results: The analysis yielded 7110, 6019, and 7747 reproducible features in plasma, EBC, and saliva, respectively. Correlations were moderate-to-strong (R = 0.41-0.80) across all pairwise comparisons of feature intensity within profiles, with the strongest between EBC and saliva. The associations of mean intensities between matrix pairs were positive and significant, controlling for subject and sampling time effects. Six out of 20 features shared in all three matrices putatively matched a list of known mobile-source air toxics.
Conclusions: Plasma, saliva, and EBC have largely comparable metabolic profiles measurable through HRM. These matrices have the potential to be used in identification and measurement of exposures to mobile-source air toxics, though further, targeted study is needed.
Figures

References
-
- Wild CP. Complementing the genome with an “exposome”: The outstanding challenge of environmental exposure measurement in molecular epidemiology. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention. 2005;14(8):1847–50. - PubMed
-
- Walker DI, Go Y-M, Liu K, Pennell KD, Jones DP. Metabolic Phenotyping in Personalized and Public Healthcare. Boston: Academic Press; 2016. Chapter 7 – Population Screening for Biological and Environmental Properties of the Human Metabolic Phenotype: Implications for Personalized Medicine; pp. 167–211.
-
- Rappaport SM. Implications of the exposome for exposure science. Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology. 2011;21(1):5–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
