Ultrasonographic evaluation of enthesitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
- PMID: 28808198
- PMCID: PMC5445219
- DOI: 10.7555/JBR.31.20160088
Ultrasonographic evaluation of enthesitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
Abstract
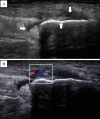
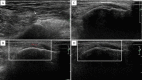
The aim of this study was to assess sensitivity and responsiveness of power Doppler ultrasound (PDUS) in detecting enthesitis for ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients compared to clinical examinations. Twenty AS patients initiating etanerceptunderwent clinical and PDUS examinations of six bilateral entheseal sites at baseline and after 1, 2 and 3 months of treatment. Clinical and PDUS examinations identified at least one entheseal lesion in nine (45%) and 19 (95%) patients, respectively. Furthermore, of 240 entheseal sites examined in these 20 patients, PDUS detected 123 entheseal lesions (51.3% of sites), compared with only 47 entheseal lesions (19.6%) detected by clinical examination (P<0.05). The entheseal lesions found on PDUS were most commonly identified by calcification (33.3%), tendon edema (29.2%), abnormal blood flow (25.8%), a thickened tendon (22.1%), cortical irregularity (12.9%), bony erosions (9.6%) and bursitis at the tendon insertion to the bone cortex (7.1%). Improvements in clinical symptoms and laboratory parameters, and significant decreases in PDUS scores were observed following treatment with etanercept. Improvements in PDUS scores continued during follow-up in patients who entered remission following treatment. In conclusion, PDUS improves detection of structural and inflammatory abnormalities of the enthesis in AS compared to physical examination. In addition, PDUS may be useful inascertaining medications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An ultrasonographic study of enthesis in early psoriatic arthritis patients naive to traditional and biologic DMARDs treatment.Rheumatol Int. 2016 Nov;36(11):1579-1583. doi: 10.1007/s00296-016-3562-8. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Rheumatol Int. 2016. PMID: 27600991
-
Clinical and ultrasonography assessment of peripheral enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011 Nov;50(11):2080-6. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker284. Epub 2011 Aug 28. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011. PMID: 21875877
-
Can power Doppler ultrasound of the entheses help in classifying recent axial spondyloarthritis? Data from the DESIR cohort.RMD Open. 2018 Aug 22;4(2):e000686. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000686. eCollection 2018. RMD Open. 2018. PMID: 30167327 Free PMC article.
-
Enthesitis in spondyloarthropathy.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1999 Jul;11(4):244-50. doi: 10.1097/00002281-199907000-00004. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1999. PMID: 10411377 Review.
-
Power Doppler ultrasonographic assessment of the ankle in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases.World J Orthop. 2014 Nov 18;5(5):574-84. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v5.i5.574. eCollection 2014 Nov 18. World J Orthop. 2014. PMID: 25405085 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radiographic entheseal lesions of the pelvic region are more prevalent in radiographic axSpA than in age- and sex-matched controls and are associated with more severe spinal disease.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Mar;44(3):1141-1150. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07345-8. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39885099 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Ultrasound Assessment of Enthesis in Psoriatic Arthritis in a Romanian Cohort.Curr Health Sci J. 2018 Oct-Dec;44(4):347-351. doi: 10.12865/CHSJ.44.04.04. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Curr Health Sci J. 2018. PMID: 31123610 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Patients With Axial Spondyloarthritis by Enthesitis Presence: Data from the Corrona Psoriatic Arthritis/Spondyloarthritis Registry.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020 Jul;2(7):449-456. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11154. Epub 2020 Jul 6. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32627974 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive Overuse Injury Causes Entheseal Damage and Palmar Muscle Fibrosis in Older Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 18;25(24):13546. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413546. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769311 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic-associated enthesitis: a review on pathophysiology, clinical relevance, diagnostic challenges, and perspective on target treatments.Immunol Res. 2025 Jul 11;73(1):106. doi: 10.1007/s12026-025-09655-0. Immunol Res. 2025. PMID: 40646307 Review.
References
-
- Amor B, Dougados M, Mijiyawa M. Criteria of the classification of spondylarthropathies[J]. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic, 1990, 57(2): 8589. - PubMed
-
- Dougados M, van der Linden S, Juhlin R, et al.The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1991, 34(10): 12181227. - PubMed
-
- Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, et al.The development of Assessment of Spondylo Arthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2009, 68(6): 777783. - PubMed
-
- Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, et al.The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for peripheral spondyloarthritis and for spondyloarthritis in general[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2011, 70(1): 2531. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

