Ginkgol C17:1 inhibits tumor growth by blunting the EGF- PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
- PMID: 28808215
- PMCID: PMC5460611
- DOI: 10.7555/JBR.31.20160039
Ginkgol C17:1 inhibits tumor growth by blunting the EGF- PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
Abstract
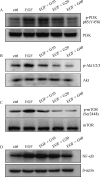
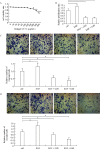
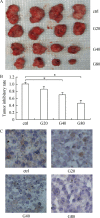
Ginkgol C17:1 has been shown to inhibit apoptosis and migration of cancer cells, but the underlying mechanisms are not fully elucidated. In this study, we explored whether the inhibitory effects of Ginkgol C17:1 were associated with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and PI3K/Akt signaling. The results showed that EGF treatment increased the phosphorylation of EGFR, PI3K, Akt, mTOR and NF-kB, and also enhanced the proliferation, migration and invasion of HepG2 cells. Ginkgol C17:1 dose-dependently inhibited EGF-induced phosphorylation/activation of all the key components including EGFR, PI3K, Akt, mTOR and NF-kB, leading to a significant reduction either of proliferation or migration and invasion of HepG2 cells. Notably, treatment with Ginkgol C17:1 in mice suppressed the growth of tumor massin vivo, and expression of EGFR in the tumor tissue. The results suggest that Ginkgol C17:1 is a potent tumor inhibiting compound that acts on EGF-induced signal transduction of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, and may represent a clinically interesting candidate for cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of ginkgol C17:1 on cisplatin-induced autophagy and apoptosis in HepG2 cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jan;15(1):1021-1029. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7398. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29399162 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of Ginkgol C17:1 on the biological behavior of tumor cells.Oncol Lett. 2017 Mar;13(3):1873-1879. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.5664. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28454337 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of ginkgol C17:1 on cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity: Protecting human normal L02 hepatocytes versus sensitizing human hepatoma HepG2 cells.Oncol Lett. 2019 Mar;17(3):3181-3190. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.9974. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30867748 Free PMC article.
-
Type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits epidermal growth factor-induced phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt signal transduction in gastric cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2013 Dec;6(6):1723-1728. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1630. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 24273605 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfated polysaccharide of Sepiella Maindroni ink inhibits the migration, invasion and matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression through suppressing EGFR-mediated p38/MAPK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in SKOV-3 cells.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Feb;107(Pt A):349-362. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.178. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 28870748
Cited by
-
Effects of ginkgol C17:1 on cisplatin-induced autophagy and apoptosis in HepG2 cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jan;15(1):1021-1029. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7398. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29399162 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Activities of Ginkgolic Acids in Relation to Autophagy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Nov 26;15(12):1469. doi: 10.3390/ph15121469. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36558920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LPS-induced extracellular AREG triggers macrophage pyroptosis through the EGFR/TLR4 signaling pathway.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 11;16:1549749. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1549749. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40292295 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Ginkgolic Acid Derivatives as SUMOylation Inhibitors.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020 Sep 24;11(11):2221-2226. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00353. eCollection 2020 Nov 12. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 33214832 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting SUMO1-mediated SUMOylation induces autophagy-mediated cancer cell death and reduces tumour cell invasion via RAC1.J Cell Sci. 2019 Oct 22;132(20):jcs234120. doi: 10.1242/jcs.234120. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31578236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prigent SA, Lemoine NR. The type 1 (EGFR-related) family of growth factor receptors and their ligands[J]. Prog Growth Factor Res, 1992, 4(1): 1–24. - PubMed
-
- Normanno N, Bianco C, De Luca A, et al. Target-based agents against ErbB receptors and their ligands: a novel approach to cancer treatment[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2003, 10(1): 1–21. - PubMed
-
- Hynes NE, MacDonald G. ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2009, 21(2): 177–184. - PubMed
-
- Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2007, 7(3): 169–181. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
