Evidence that Listeria innocua modulates its membrane's stored curvature elastic stress, but not fluidity, through the cell cycle
- PMID: 28808346
- PMCID: PMC5556093
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-06855-z
Evidence that Listeria innocua modulates its membrane's stored curvature elastic stress, but not fluidity, through the cell cycle
Abstract
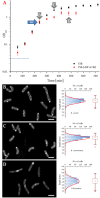
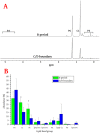
This paper reports that the abundances of endogenous cardiolipin and phosphatidylethanolamine halve during elongation of the Gram-positive bacterium Listeria innocua. The lyotropic phase behaviour of model lipid systems that describe these modulations in lipid composition indicate that the average stored curvature elastic stress of the membrane is reduced on elongation of the cell, while the fluidity appears to be maintained. These findings suggest that phospholipid metabolism is linked to the cell cycle and that changes in membrane composition can facilitate passage to the succeding stage of the cell cycle. This therefore suggests a means by which bacteria can manage the physical properties of their membranes through the cell cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cell cycle dependent changes in membrane stored curvature elastic energy: evidence from lipidomic studies.Faraday Discuss. 2013;161:481-97; discussion 563-89. doi: 10.1039/c2fd20078c. Faraday Discuss. 2013. PMID: 23805754
-
Novel tilt-curvature coupling in lipid membranes.J Chem Phys. 2017 Aug 28;147(8):084702. doi: 10.1063/1.4990404. J Chem Phys. 2017. PMID: 28863515
-
Mammalian phospholipid homeostasis: evidence that membrane curvature elastic stress drives homeoviscous adaptation in vivo.J R Soc Interface. 2016 Aug;13(121):20160228. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2016.0228. J R Soc Interface. 2016. PMID: 27534697 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid domains in bacterial membranes.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Sep;61(5):1110-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05317.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16925550 Review.
-
Bacterial Membranes: Structure, Domains, and Function.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2017 Sep 8;71:519-538. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-102215-095630. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28697671 Review.
Cited by
-
Sterol and lipid metabolism in bees.Metabolomics. 2023 Aug 29;19(9):78. doi: 10.1007/s11306-023-02039-1. Metabolomics. 2023. PMID: 37644282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high-throughput platform for detailed lipidomic analysis of a range of mouse and human tissues.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020 May;412(12):2851-2862. doi: 10.1007/s00216-020-02511-0. Epub 2020 Mar 7. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32144454 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Metabolites of Marine Origin Have Unusual Effects on Model Membrane Systems.Mar Drugs. 2020 Feb 19;18(2):125. doi: 10.3390/md18020125. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32092956 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-icing properties of polar bear fur.Sci Adv. 2025 Jan 31;11(5):eads7321. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ads7321. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 39879302 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma-derived exosome-like vesicles are enriched in lyso-phospholipids and pass the blood-brain barrier.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 21;15(9):e0232442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232442. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32956358 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

