Effects of air-abrasion pressure on the resin bond strength to zirconia: a combined cyclic loading and thermocycling aging study
- PMID: 28808637
- PMCID: PMC5553020
- DOI: 10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.206
Effects of air-abrasion pressure on the resin bond strength to zirconia: a combined cyclic loading and thermocycling aging study
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the combined effect of fatigue cyclic loading and thermocycling (CLTC) on the shear bond strength (SBS) of a resin cement to zirconia surfaces that were previously air-abraded with aluminum oxide (Al2O3) particles at different pressures.
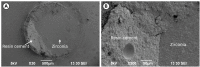
Materials and methods: Seventy-two cuboid zirconia specimens were prepared and randomly assigned to 3 groups according to the air-abrasion pressures (1, 2, and 2.8 bar), and each group was further divided into 2 groups depending on aging parameters (n = 12). Panavia F 2.0 was placed on pre-conditioned zirconia surfaces, and SBS testing was performed either after 24 hours or 10,000 fatigue cycles (cyclic loading) and 5,000 thermocycles. Non-contact profilometry was used to measure surface roughness. Failure modes were evaluated under optical and scanning electron microscopy. The data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance and χ2 tests (α = 0.05).
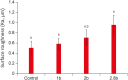
Results: The 2.8 bar group showed significantly higher surface roughness compared to the 1 bar group (p < 0.05). The interaction between pressure and time/cycling was not significant on SBS, and pressure did not have a significant effect either. SBS was significantly higher (p = 0.006) for 24 hours storage compared to CLTC. The 2 bar-CLTC group presented significantly higher percentage of pre-test failure during fatigue compared to the other groups. Mixed-failure mode was more frequent than adhesive failure.
Conclusions: CLTC significantly decreased the SBS values regardless of the air-abrasion pressure used.
Keywords: Air-abrasion; Bond strength; Fatigue; Panavia F 2.0; Resin cement; Thermocycling.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Lazar DR, Bottino MC, Özcan M, Valandro LF, Amaral R, Ussui V, Bressiani AH. Y-TZP ceramic processing from coprecipitated powders: a comparative study with three commercial dental ceramics. Dent Mater. 2008;24:1676–1685. - PubMed
-
- Luangruangrong P, Cook NB, Sabrah AH, Hara AT, Bottino MC. Influence of full-contour zirconia surface roughness on wear of glass-ceramics. J Prosthodont. 2014;23:198–205. - PubMed
-
- Lawson NC, Burgess JO. Dental ceramics: a current review. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2014;35:161–166. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Aboushelib MN, Feilzer AJ. Strength influencing variables on CAD/CAM zirconia frameworks. Dent Mater. 2008;24:633–638. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

