The Sydney Heart Bank: improving translational research while eliminating or reducing the use of animal models of human heart disease
- PMID: 28808947
- PMCID: PMC5578936
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-017-0305-3
The Sydney Heart Bank: improving translational research while eliminating or reducing the use of animal models of human heart disease
Erratum in
-
Correction to: The Sydney Heart Bank: improving translational research while eliminating or reducing the use of animal models of human heart disease.Biophys Rev. 2018 Jun;10(3):941. doi: 10.1007/s12551-018-0397-4. Biophys Rev. 2018. PMID: 29388160 Free PMC article.
Abstract
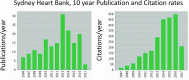
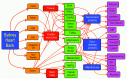
The Sydney Heart Bank (SHB) is one of the largest human heart tissue banks in existence. Its mission is to provide high-quality human heart tissue for research into the molecular basis of human heart failure by working collaboratively with experts in this field. We argue that, by comparing tissues from failing human hearts with age-matched non-failing healthy donor hearts, the results will be more relevant than research using animal models, particularly if their physiology is very different from humans. Tissue from heart surgery must generally be used soon after collection or it significantly deteriorates. Freezing is an option but it raises concerns that freezing causes substantial damage at the cellular and molecular level. The SHB contains failing samples from heart transplant patients and others who provided informed consent for the use of their tissue for research. All samples are cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen within 40 min of their removal from the patient, and in less than 5-10 min in the case of coronary arteries and left ventricle samples. To date, the SHB has collected tissue from about 450 failing hearts (>15,000 samples) from patients with a wide range of etiologies as well as increasing numbers of cardiomyectomy samples from patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The Bank also has hearts from over 120 healthy organ donors whose hearts, for a variety of reasons (mainly tissue-type incompatibility with waiting heart transplant recipients), could not be used for transplantation. Donor hearts were collected by the St Vincent's Hospital Heart and Lung transplantation team from local hospitals or within a 4-h jet flight from Sydney. They were flushed with chilled cardioplegic solution and transported to Sydney where they were quickly cryopreserved in small samples. Failing and/or donor samples have been used by more than 60 research teams around the world, and have resulted in more than 100 research papers. The tissues most commonly requested are from donor left ventricles, but right ventricles, atria, interventricular system, and coronary arteries vessels have also been reported. All tissues are stored for long-term use in liquid N or vapor (170-180 °C), and are shipped under nitrogen vapor to avoid degradation of sensitive molecules such as RNAs and giant proteins. We present evidence that the availability of these human heart samples has contributed to a reduction in the use of animal models of human heart failure.
Keywords: Healthy donor human hearts; Human heart failure; Human heart tissue bank; Reducing the use of animals in research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
CG dos Remedios declares that he has no conflicts of interest. SP Lal declares that he has no conflicts of interest. J McNamara declares that he has no conflicts of interest. A Keogh declares that she has no conflicts of interest. PS Macdonald declares that he has no conflicts of interest. R Cooke declares that he has no conflicts of interest. E Ehler declares that she has no conflicts of interest. R Knöll declares that he has no conflicts of interest. SB Marston declares that he has no conflicts of interest. J Stelzer declares that he has no conflicts of interest. H Granzier declares that he has no conflicts of interest. C Bezzina declares that she has no conflicts of interest. S van Dijk declares that she has no conflicts of interest. F De Man declares that she has no conflicts of interest. GJM Stienen declares that he has no conflicts of interest. J Odeberg declares that he has no conflicts of interest. F Pontén declares that he has no conflicts of interest. W Linke declares that he has no conflicts of interest. J van der Velden declares that she has no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Bang ML, Centner T, Fornoff F, Geach AJ, Gotthardt M, McNabb M, Witt CC, Labeit D, Gregorio CC, Granzier H, Labeit S. The complete gene sequence of titin, expression of an unusual approximately 700-kDa titin isoform, and its interaction with obscurin identify a novel Z-line to I-band linking system. Circ Res. 2001;89:1065–1072. doi: 10.1161/hh2301.100981. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berry D, Balcar VJ, Barden JA, Keogh A, dos Remedios CG (2000) Changes in P2X1 receptors in human left ventricles and their relationship to the acto-ATPase α-sarcoglycan (adhalin). Electrophoresis 17: 3857-3862 - PubMed
-
- Cordell HJ, Bentham J, Topf A, Zelenika D, Heath S, Mamasoula C, Cosgrove C, Blue G, Granados-Riveron J, Setchfield K, Thornborough C, Breckpot J, Soemedi R, Martin R, Rahman TJ, Hall D, van Engelen K, Moorman AF, Zwinderman AH, Barnett P, Koopmann TT, Adriaens ME, Varro A, George AL, Jr, dos Remedios C, Bishopric NH, Bezzina CR, O’Sullivan J, Gewillig M, Bu’lock FA, Winlaw D, Bhattacharya S, Devriendt K, Brook JD, Mulder BJ, Mital S, Postma AV, Lathrop GM, Farrall M, Goodship JA, Keavney BD. Genome-wide association study of multiple congenital heart disease phenotypes identifies a susceptibility locus for atrial septal defect at chromosome 4p16. Nat Genet. 2013;45:822–824. doi: 10.1038/ng.2637. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

