Color and power Doppler combined with Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) to evaluate the fetal heart
- PMID: 28809063
- PMCID: PMC5656930
- DOI: 10.1002/uog.17522
Color and power Doppler combined with Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) to evaluate the fetal heart
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the performance of color and bidirectional power Doppler ultrasound combined with Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE) in examining the fetal heart.
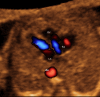
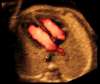
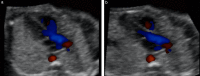
Methods: A prospective cohort study was conducted of fetuses in the second and third trimesters with a normal heart or with congenital heart disease (CHD). One or more spatiotemporal image correlation (STIC) volume datasets, combined with color or bidirectional power Doppler (S-flow) imaging, were acquired in the apical four-chamber view. Each successfully obtained STIC volume was evaluated by STICLoop™ to determine its appropriateness before applying the FINE method. Visualization rates for standard fetal echocardiography views using diagnostic planes and/or Virtual Intelligent Sonographer Assistance (VIS-Assistance®) were calculated for grayscale (removal of Doppler signal), color Doppler and S-flow Doppler. In four cases with CHD (one case each of tetralogy of Fallot, hypoplastic left heart and coarctation of the aorta, interrupted inferior vena cava with azygos vein continuation and asplenia, and coarctation of the aorta with tricuspid regurgitation and hydrops), the diagnostic potential of this new technology was presented.
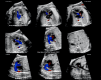
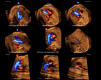
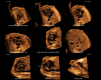
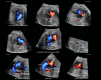
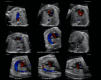
Results: A total of 169 STIC volume datasets of the normal fetal heart (color Doppler, n = 78; S-flow Doppler, n = 91) were obtained from 37 patients. Only a single STIC volume of color Doppler and/or a single volume of S-flow Doppler per patient were analyzed using FINE. Therefore, 60 STIC volumes (color Doppler, n = 27; S-flow Doppler, n = 33) comprised the final study group. Median gestational age at sonographic examination was 23 (interquartile range, 21-27.5) weeks. Color Doppler FINE generated nine fetal echocardiography views (grayscale) using (1) diagnostic planes in 73-100% of cases, (2) VIS-Assistance in 100% of cases, and (3) a combination of diagnostic planes and/or VIS-Assistance in 100% of cases. The rate of generating successfully eight fetal echocardiography views with appropriate color and S-flow Doppler information was 89-100% and 91-100% of cases, respectively, using a combination of diagnostic planes and/or VIS-Assistance. However, the success rate for the ninth echocardiography view (i.e. superior and inferior venae cavae) was 33% and 30% for color and S-flow Doppler, respectively. In all four cases of CHD, color Doppler FINE demonstrated evidence of abnormal fetal cardiac anatomy and/or hemodynamic flow.
Conclusions: The FINE method applied to STIC volumes of normal fetal hearts acquired with color or bidirectional power Doppler information can generate successfully eight to nine standard fetal echocardiography views (via grayscale, color Doppler or power Doppler) in the second and third trimesters. In cases of CHD, color Doppler FINE demonstrates successfully abnormal anatomy and/or Doppler flow characteristics. Published 2017. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Keywords: 4D; 5D heart color; STIC; cardiac; congenital heart disease; fetal echocardiography; spatiotemporal image correlation; ultrasound.
Published 2017. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Figures
References
-
- Kremkau FK. Principles of color flow imaging. J Vasc Tech 1991; 15: 104–109.
-
- Omoto R, Kasai C. Physics and instrumentation of Doppler color flow mapping. Echocardiography 1987; 4: 467–483.
-
- Lee R. Physical principles of flow mapping in cardiology In Textbook of Color Doppler Echocardiography, Nanda NC. (ed). Lea & Febiger: Philadelphia, 1989; 18.
-
- Maulik D. Sonographic color flow mapping: basic principles In Doppler Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology, Maulik D. (ed). Springer‐Verlag: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005; 69–84.
-
- Carvalho JS, Allan LD, Chaoui R, Copel JA, DeVore GR, Hecher K, Lee W, Munoz H, Paladini D, Tutschek B, Yagel S. ISUOG practice guidelines (updated): sonographic screening examination of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 41: 348–359. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

