An Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Immunosensor for HIV p24 Based on Fe₃O₄@SiO₂ Nanomagnetic Probes and Nanogold Colloid-Labeled Enzyme-Antibody Copolymer as Signal Tag
- PMID: 28809208
- PMCID: PMC5452317
- DOI: 10.3390/ma6041255
An Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Immunosensor for HIV p24 Based on Fe₃O₄@SiO₂ Nanomagnetic Probes and Nanogold Colloid-Labeled Enzyme-Antibody Copolymer as Signal Tag
Abstract
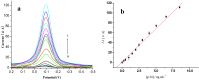
An ultrasensitive portable electrochemical immunosensor for human immunodeficiency virus p24 (HIV p24) antigen detection has been developed, whereby the detection sensitivity was 1000 times higher than that of the ELISA method. Firstly, a novel HRP enzyme-antibody copolymer (EV-p24 Ab2) was synthesized through an EnVision regent (EV, a dextrin amine skeleton anchoring more than 100 molecules of HRP and 15 molecules of anti IgG), then incubated in the secondary antibody of p24. Secondly, the copolymer was immobilized on the gold nanocolloids (AuNPs) to fabricate a novel signal tag (AuNPs/EV-p24 Ab2). Subsequently, a sandwich-type immunoreaction would take place between the capture probe (silicon dioxide-coated magnetic Fe₃O₄ nanoparticles (MNPs) labeled with the primary p24 antibody (MNPs-p24 Ab1)), p24 (different concentrations) and the signal tag [AuNPs/EV-p24 Ab2)] to form the immunocomplex. Finally, the immunocomplex was absorbed on the surface of screen printed carbon electrode (SPCE) by a magnet and immersed in the o-hydroxyl phenol (HQ) and H₂O₂. The large amounts of HRP on the signal tag can catalyze the oxidation of HQ by H₂O₂, which can induce an amplified reductive current. Moreover, the capture probe could improve the accumulation ability of p24 and facilitate its separation from the substrate through the magnet. Under optimal conditions, the proposed immunoassay exhibited good sensitivity to p24 within a certain concentration range from 0.001 to 10.00 ng/mL, with a detection limit of 0.5 pg/mL (S/N = 3). The proposed method can be used for real-time and early detection of HIV-infected people.
Keywords: Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic beads; HIV p24; electrochemical immunosensor; nanogold-labeled EnVision antibody enzyme complex; signal amplification.
Figures






References
-
- Spacek L.A., Lutwama F., Shihab H.M., Summerton J., Kamya M.R., Ronald A., Laeyendecker O., Quinn T.C., Mayanja-Kizza H. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasensitive heat-denatured HIV-1 p24 antigen in non-B subtypes in Kampala, Uganda. Int. J. STD AIDS. 2011;22:310–314. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2009.009363. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kivuyo S.L., Johannessen A., Trøseid D., Kasubi M.J., Gundersen S.G., Naman E., Mushi D., Ngowi B.J., Mfinanga G.S., Bruun J.N. p24 antigen detection on dried blood spots is a feasible and reliable test for infant HIV infection in rural Tanzania. Int. J. STD AIDS. 2011;22:719–721. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2009.009382. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tshishi T.A., Ditu S.M., Kabwe B.M., Philomène M.K., Anaclet S.B. A sensitive radioimmunoassay of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 p24 antigen in serum. Immuno-Anal. Biol. Spéc. 2007;22:190–193.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

