Nanomagnetic Gene Transfection for Non-Viral Gene Delivery in NIH 3T3 Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts
- PMID: 28809306
- PMCID: PMC5452119
- DOI: 10.3390/ma6010255
Nanomagnetic Gene Transfection for Non-Viral Gene Delivery in NIH 3T3 Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts
Abstract
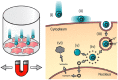
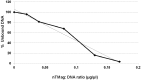
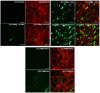
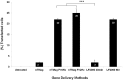
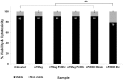
The objective of this work was to examine the potential of oscillating nanomagnetic gene transfection systems (magnefect-nano™) for improving the transfection efficiency of NIH3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) in comparison to other non-viral transfection techniques-static magnetofection™ and the cationic lipid agent, Lipofectamine 2000™. Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) associated with the plasmid coding for green fluorescent protein (GFP) were used to transfect NIH3T3 cells. The magnefect-nano system was evaluated for transfection efficiency, and any potential associated effects on cell viability were investigated. MNPs associated with the plasmid coding for GFP were efficiently delivered into NIH3T3 cells, and the magnefect-nano system significantly enhanced overall transfection efficiency in comparison to lipid-mediated gene delivery. MNP dosage used in this work was not found to affect the cell viability and/or morphology of the cells. Non-viral transfection using MNPs and the magnefect-nano system can be used to transfect NIH3T3 cells and direct reporter gene delivery, highlighting the wide potential of nanomagnetic gene transfection in gene therapy.
Keywords: DNA; magnetic field; magnetic nanoparticles; nanomagnetic gene transfection; non-viral gene transfection.
Figures
References
-
- Cho H.J., Lee T.S., Park J.B., Park K.K., Choe J.Y., Sin D.I., Park Y.Y., Moon Y.S., Lee K.G., Yeo J.H., et al. Disulfiram suppresses invasive ability of osteosarcoma cells via the inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007;40:1069–1076. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2007.40.6.1069. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kersting C., Gebert C., Agelopoulos K., Schmidt H., van Diest P.J., Juergens H., Winkelmann W., Kevric M., Gosheger G., Brandt B., et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in high-grade osteosarcoma is associated with a good clinical outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007;13:2998–3005. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2432. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lamoureux F., Richard P., Wittrant Y., Battaglia S., Pilet P., Trichet V., Blanchard F., Gouin F., Pitard B., Heymann D., Redini F. Therapeutic relevance of osteoprotegerin gene therapy in osteosarcoma: Blockage of the vicious cycle between tumor cell proliferation and bone resorption. Cancer Res. 2007;67:7308–7318. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

