Effect of an Intensive Lifestyle Intervention on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 28810024
- PMCID: PMC5817591
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2017.10169
Effect of an Intensive Lifestyle Intervention on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: It is unclear whether a lifestyle intervention can maintain glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Objective: To test whether an intensive lifestyle intervention results in equivalent glycemic control compared with standard care and, secondarily, leads to a reduction in glucose-lowering medication in participants with type 2 diabetes.
Design, setting, and participants: Randomized, assessor-blinded, single-center study within Region Zealand and the Capital Region of Denmark (April 2015-August 2016). Ninety-eight adult participants with non-insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes who were diagnosed for less than 10 years were included. Participants were randomly assigned (2:1; stratified by sex) to the lifestyle group (n = 64) or the standard care group (n = 34).
Interventions: All participants received standard care with individual counseling and standardized, blinded, target-driven medical therapy. Additionally, the lifestyle intervention included 5 to 6 weekly aerobic training sessions (duration 30-60 minutes), of which 2 to 3 sessions were combined with resistance training. The lifestyle participants received dietary plans aiming for a body mass index of 25 or less. Participants were followed up for 12 months.
Main outcomes and measures: Primary outcome was change in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) from baseline to 12-month follow-up, and equivalence was prespecified by a CI margin of ±0.4% based on the intention-to-treat population. Superiority analysis was performed on the secondary outcome reductions in glucose-lowering medication.
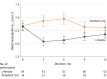
Results: Among 98 randomized participants (mean age, 54.6 years [SD, 8.9]; women, 47 [48%]; mean baseline HbA1c, 6.7%), 93 participants completed the trial. From baseline to 12-month follow-up, the mean HbA1c level changed from 6.65% to 6.34% in the lifestyle group and from 6.74% to 6.66% in the standard care group (mean between-group difference in change of -0.26% [95% CI, -0.52% to -0.01%]), not meeting the criteria for equivalence (P = .15). Reduction in glucose-lowering medications occurred in 47 participants (73.5%) in the lifestyle group and 9 participants (26.4%) in the standard care group (difference, 47.1 percentage points [95% CI, 28.6-65.3]). There were 32 adverse events (most commonly musculoskeletal pain or discomfort and mild hypoglycemia) in the lifestyle group and 5 in the standard care group.
Conclusions and relevance: Among adults with type 2 diabetes diagnosed for less than 10 years, a lifestyle intervention compared with standard care resulted in a change in glycemic control that did not reach the criterion for equivalence, but was in a direction consistent with benefit. Further research is needed to assess superiority, as well as generalizability and durability of findings.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT02417012.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Intensive Lifestyle Intervention for Type 2 Diabetes.JAMA. 2017 Dec 26;318(24):2494. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.17232. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 29279921 No abstract available.
References
-
- American Diabetes Association 6. Obesity Management for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(suppl 1):S47-S51. - PubMed
-
- Gorter KJ, van de Laar FA, Janssen PG, Houweling ST, Rutten GE. Diabetes: glycaemic control in type 2 (drug treatments). http://clinicalevidence.bmj.com/x/systematic-review/0609/overview.html. Accessed July 4, 2017. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holman RR, Thorne KI, Farmer AJ, et al. ; 4-T Study Group . Addition of biphasic, prandial, or basal insulin to oral therapy in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(17):1716-1730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

